Mud rotary geotechnical drilling is a vital technique for obtaining reliable soil data needed in construction projects. By using a mixture of water and clay-based mud, this method ensures smooth drilling through difficult soil layers, making it ideal for deep, challenging sites.
Accurate soil testing is crucial for determining foundation suitability and preventing structural issues, making mud rotary drilling an essential tool for engineers and builders alike. This technique provides consistent results, enabling informed decisions and long-term project success.
What is Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling
Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling is a drilling method commonly used in geotechnical investigations to explore soil and rock conditions beneath the ground surface. It involves using a mixture of water and clay-based mud, which is pumped down the drill pipe to cool the bit, stabilize the borehole, and remove cuttings.
This technique allows for efficient drilling in difficult soil types and provides vital information for evaluating foundation stability, soil properties, and groundwater conditions in construction and engineering projects.
How Does Mud Rotary Drilling Work?
Mud Rotary Drilling works by using a specialized drilling rig that circulates a mixture of water and clay-based mud through the drill bit and up the borehole. The mud serves multiple purposes: it cools the drill bit, stabilizes the borehole, and helps carry rock cuttings to the surface.
As the drill bit penetrates the soil, the slurry acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and preventing the bit from overheating, while also preventing the collapse of the borehole walls, especially in loose or unconsolidated soil types.
The drilling process involves continuous circulation of the mud, which flows down the drill pipe and back up the annular space between the pipe and borehole. As the bit progresses, the soil and rock cuttings are suspended in the mud and brought to the surface for analysis.
The mud drilling method provides accurate and undisturbed samples, which are essential for geotechnical investigations and foundation design. Additionally, the mud mixture can be adjusted with various additives to suit different soil conditions, making Mud Rotary Drilling versatile for a wide range of geotechnical applications.
Why Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling?
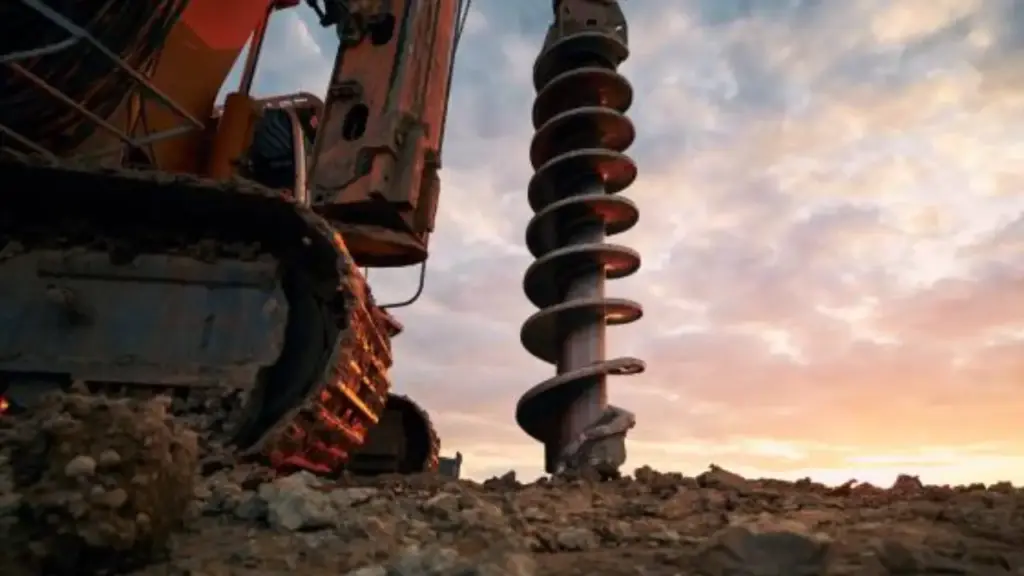

Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling is crucial in providing reliable subsurface data for construction and engineering projects. By efficiently accessing deep soil and rock layers, it ensures accurate assessments of foundation conditions, soil properties, and groundwater levels.
This method enhances project safety, minimizes risks, and supports the development of stable, durable structures. Its ability to tackle challenging soil conditions and provide undisturbed samples makes it an essential tool for informed decision-making in construction, environmental studies, and infrastructure planning.
- Efficient in Challenging Soil Conditions: The mud helps stabilize the borehole, allowing for smooth drilling through difficult formations like clay, shale, or unconsolidated sands.
- Accurate Soil and Rock Sampling: The use of mud ensures that soil and rock samples are collected without contamination, providing reliable data for foundation design, slope stability, and construction planning.
- Enhanced Borehole Stability: The mud slurry creates a stable environment by preventing the collapse of the borehole walls, especially in loose or unstable soil, reducing drilling time and risks.
- Improved Drilling Speed: By cooling the drill bit and carrying cuttings to the surface, the mud rotary method increases drilling speed compared to other methods, making projects more cost-effective.
- Versatility in Depth and Reach: Mud rotary drilling can reach significant depths and handle a variety of ground conditions, making it ideal for deep exploration projects, such as foundation analysis for high-rise buildings or dams.
This combination of efficiency, reliability, and versatility makes Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling a top choice for modern soil testing and geotechnical investigations.
Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling Applications
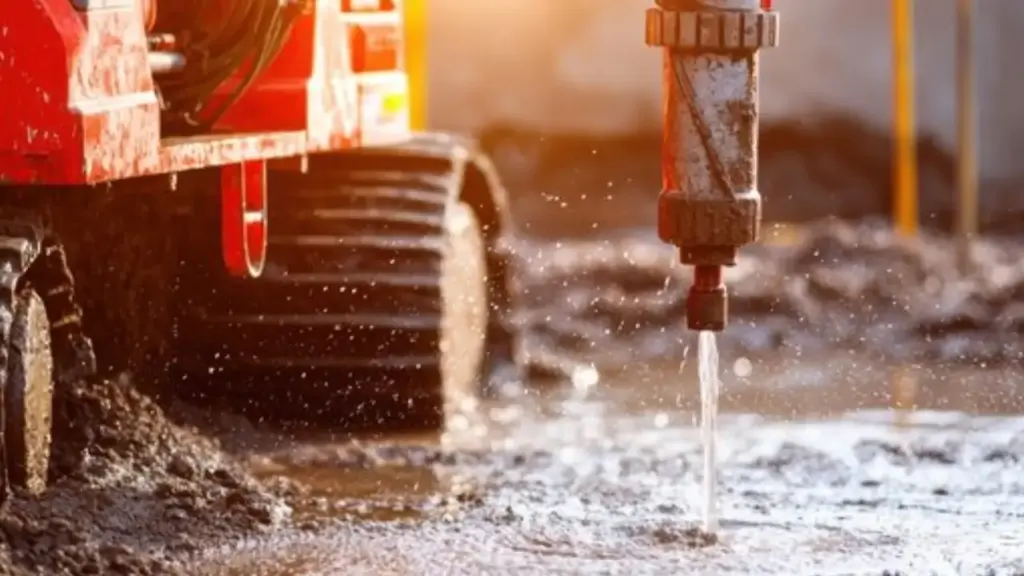

Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling is widely used across various industries for its ability to gather detailed subsurface information, ensuring that construction and engineering projects are based on solid data. It plays a key role in the exploration of soil and rock properties, groundwater levels, and the stability of the land for various structures. This drilling technique is essential for geotechnical investigations, foundation design, and environmental monitoring.
Common Applications of mud rotary geotechnical drilling Include:
- Foundation Investigation: Helps determine the soil’s bearing capacity and stability, crucial for designing safe and durable foundations.
- Environmental Studies: Assists in assessing groundwater contamination, soil composition, and site conditions for environmental remediation projects.
- Geotechnical Surveys: Provides accurate data for engineers to evaluate the suitability of land for construction, mining, or civil engineering projects.
- Seismic and Structural Studies: Used to obtain samples that are essential in studying seismic risks and understanding subsurface conditions that affect building integrity.
- Water Well Drilling: Applied in creating wells for water exploration or monitoring groundwater levels in different geological formations.
What is Needed for Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling?
Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling requires a combination of specialized equipment, skilled operators, and proper materials to ensure efficient and accurate subsurface exploration. The drilling process relies heavily on a mud mixture, which acts as a coolant and stabilizer, and requires the right tools for safe and effective operations.
A well-equipped drilling rig, along with necessary safety measures, is also essential for tackling different soil conditions.
Key Requirements Include:
- Drilling Rig: A robust and powerful rig capable of reaching desired depths and handling the mud slurry to prevent borehole collapse.
- Mud Pump System: Ensures a continuous flow of drilling mud to the bit, providing cooling, lubrication, and cuttings removal.
- Drill Bit: Specialized bits, often made of hard materials like tungsten carbide, are used to break through various soil layers and rocks efficiently.
- Drilling Mud: A mixture of water, clay, and additives that helps stabilize the borehole, cool the bit, and transport soil cuttings to the surface.
- Sampling Tools: Tools like split spoons or Shelby tubes are used to collect undisturbed soil and rock samples for testing.
- Safety Equipment: Personal protective gear and safety systems, such as fall protection, for the crew to ensure safe operations in challenging environments.
- Experienced Operators: Skilled drillers are essential for managing the equipment, maintaining safety, and ensuring the accuracy of collected data.
What Are the Advantages of Mud Rotary Drilling?
Mud Rotary Drilling offers several distinct advantages that make it a preferred choice for geotechnical investigations. The use of mud as a drilling fluid helps stabilize the borehole and provides better control over drilling conditions, especially in challenging soils.
This mud drilling method allows for more efficient, reliable, and accurate sampling, which is crucial for informed decision-making in construction, environmental, and engineering projects.
Key Advantages Include:
- Enhanced Borehole Stability: The drilling mud keeps the borehole walls from collapsing, particularly in loose, sandy, or unstable soils, allowing for deeper exploration without compromising safety.
- Efficient Drilling in Tough Conditions: The mud slurry cools the drill bit and transports soil cuttings to the surface, enabling faster and more efficient drilling through challenging formations like clay, shale, or gravel.
- Accurate Sampling: The use of mud ensures that undisturbed soil and rock samples are collected with minimal contamination, providing high-quality data for foundation analysis and material testing.
- Reduced Risk of Well Contamination: The mud acts as a barrier between the borehole and surrounding soil, reducing the likelihood of cross-contamination, particularly in environmental drilling projects.
- Cost-Effective for Deep Drilling: Mud rotary drilling can efficiently reach significant depths, reducing the time and cost compared to other drilling methods, making it ideal for deep geotechnical investigations or water well drilling.
- Versatility in Different Soil Types: The technique can be used in a wide range of soil conditions, from soft sands to hard rock, offering a versatile solution for various geotechnical applications.
What is the Difference Between Air Rotary and Mud Rotary?
Air Rotary and Mud Rotary are two common drilling methods used for geotechnical investigations, each with its unique advantages and limitations.
Understanding the differences in their operation, efficiency, sample quality, environmental impact, and costs can help determine the best method for specific projects.
Drilling Fluid
Air Rotary uses compressed air to flush out cuttings from the borehole, making it suitable for dry, soft soils. Mud Rotary, on the other hand, uses a water-based mud slurry that cools the drill bit and stabilizes the borehole, especially in unstable soils.
Drilling Efficiency
Air Rotary tends to be faster in unconsolidated or softer soils because the compressed air clears out debris quickly. However, it may struggle with harder formations and can be less efficient in achieving precise depth. Mud Rotary, though slower, handles challenging conditions better, offering more control and stability in deep drilling.
Sample Quality
Mud Rotary is better for collecting undisturbed soil samples as the mud helps keep the sample intact while minimizing contamination. The continuous flow of mud prevents soil disturbance during the extraction of samples, which is crucial for accurate geotechnical testing. Air Rotary often disturbs the soil, making sample quality less reliable.
Environmental Impact
Air Rotary is considered more environmentally friendly because it generates minimal waste, as compressed air doesn’t produce slurry. It’s a cleaner option, especially in sensitive environmental areas. In contrast, Mud Rotary involves the disposal of large volumes of mud, which can pose challenges for waste management and environmental safety.
Cost and Maintenance
Air Rotary systems are generally more cost-effective in terms of both operational and maintenance costs because air compressors are relatively inexpensive and simpler to maintain. Mud Rotary rigs, however, incur higher operational costs due to the need for specialized mud pumps and disposal of drilling fluids, as well as additional maintenance for handling complex equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mud rotary geotechnical drilling is an invaluable method for accurate soil testing, offering reliable data for construction projects. Its ability to handle challenging soil conditions and provide detailed subsurface insights makes it essential for successful foundation planning.
Utilizing the right tools ensures the drilling process is efficient and precise. For quality and performance, Sinodrills offers a wide range of Mud Rotary Geotechnical Drilling equipment tailored to meet industry needs.
Investing in advanced mud rotary geotechnical drilling tools from Sinodrills enhances project reliability and minimizes risks.