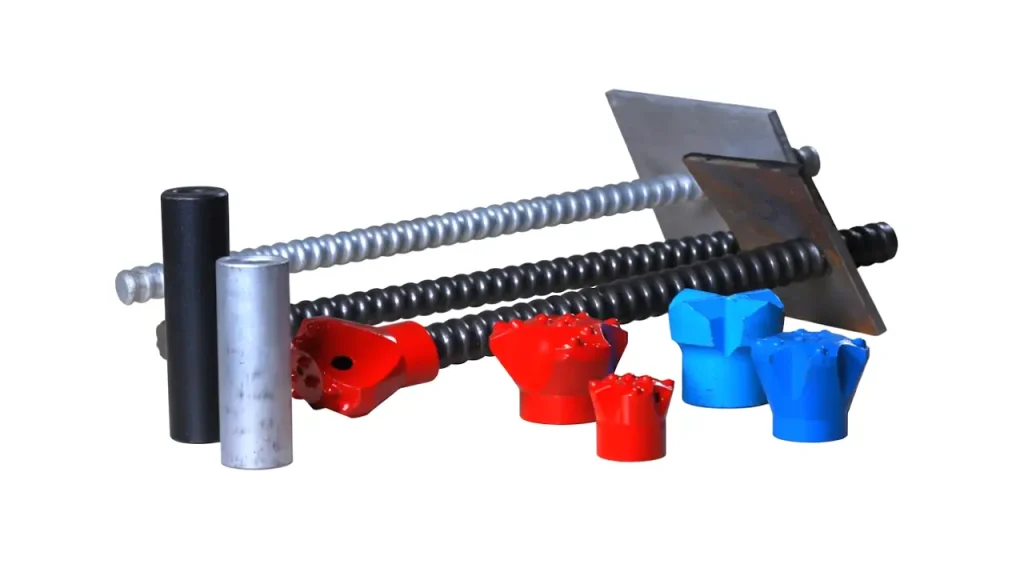
Self-drilling anchors are an innovative solution for rock and soil stabilization, offering efficiency and reliability in challenging ground conditions. This guide will walk you through the essential steps for proper installation, ensuring a successful and durable outcome for your projects.
Learn how to effectively deploy these versatile anchors, from understanding the components to mastering the drilling and grouting processes. We’ll provide practical tips and insights to help you achieve optimal performance and safety.
What are Self Drilling Anchors?
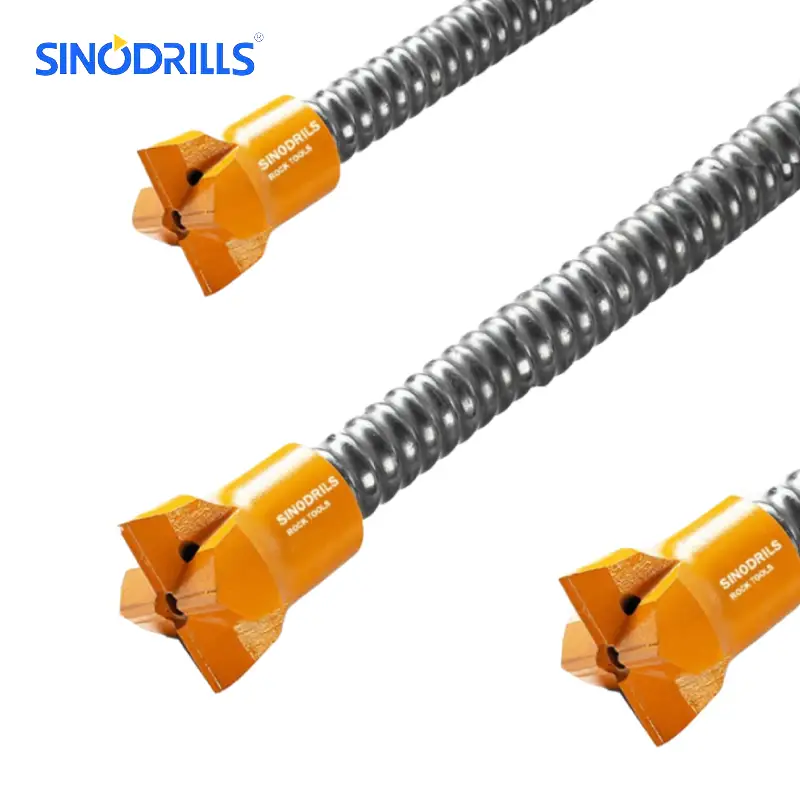
Self-drilling anchors, often used in geotechnical and civil engineering applications, are an innovative type of anchor system designed for efficiency in challenging ground conditions. Unlike traditional anchors that require a pre-drilled hole, these anchors combine the drilling and anchoring process into a single, continuous operation.
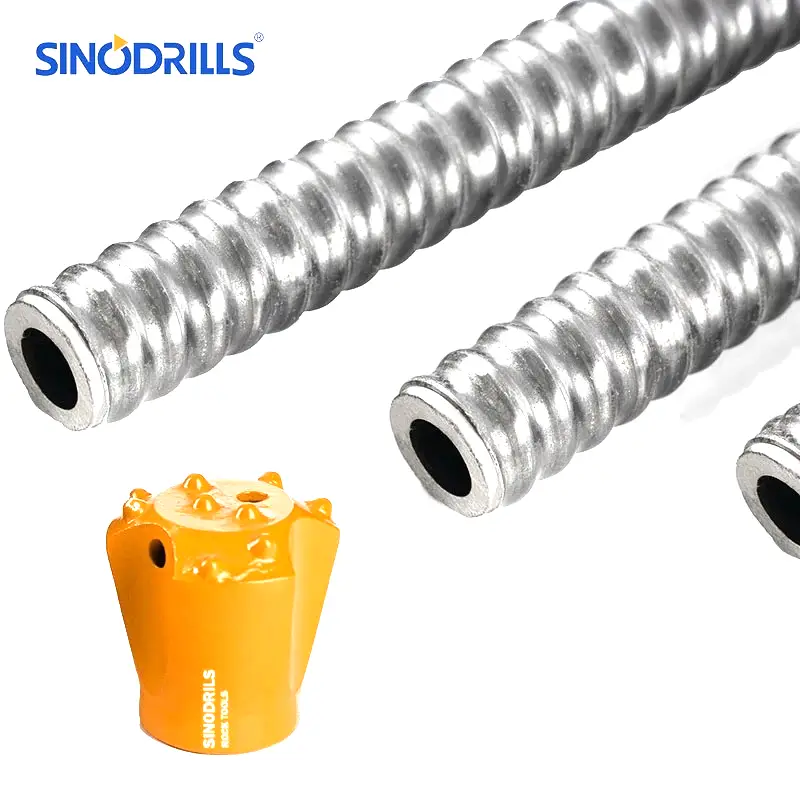
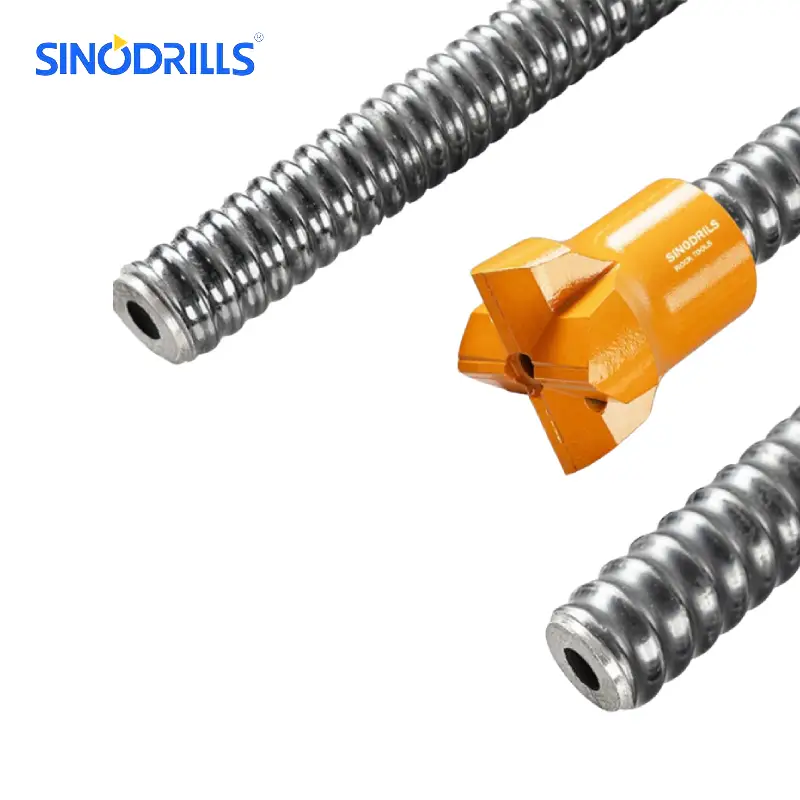
They typically consist of a hollow bar with a sacrificial drill bit at one end, which drills into the ground while simultaneously allowing for the injection of grout or other binding agents through the hollow core.
This integrated approach is particularly beneficial in loose soils, fractured rock, or collapsing boreholes, as it stabilizes the hole as it’s being drilled and creates a strong, permanent bond with the surrounding material.
Recommended Self-Drilling Anchors
How to Install Self-Drilling Anchors?
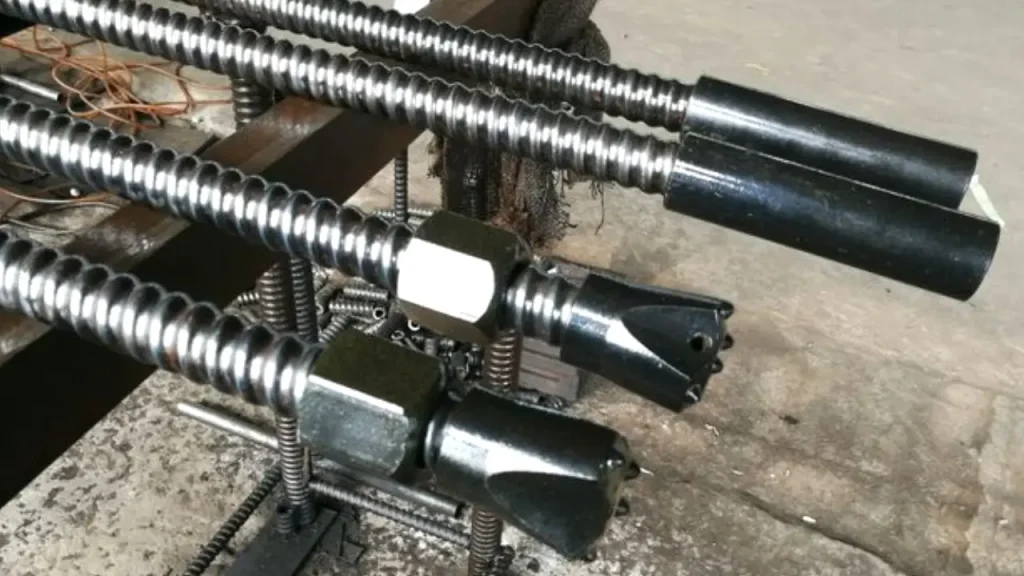

Self-drilling anchors represent a significant advancement in ground engineering, providing an integrated and highly efficient solution for various geotechnical and civil construction applications. Their unique design combines the functions of drilling and anchoring into a single, continuous operation, which is particularly advantageous in challenging and unstable ground conditions.
This innovative approach not only simplifies the installation process but also enhances the overall stability and reliability of the anchorage system.
Step 1: Site Investigation and Design
The initial and most critical step involves a thorough site investigation to understand the subsurface conditions. This includes geological surveys, soil sampling, and laboratory testing to determine soil and rock properties, groundwater levels, and potential geological hazards.
Based on this data, engineers design the self-drilling anchor system, specifying the anchor type, diameter, length, drill bit type, and grouting parameters. This design phase ensures the anchors are appropriately sized and positioned to meet the structural requirements and provide the necessary load-bearing capacity.
Simultaneously, a detailed review of site accessibility, utility locations, and environmental considerations is conducted. This comprehensive understanding allows for the creation of a detailed installation plan, including equipment selection, safety protocols, and a project timeline. Proper planning at this stage minimizes unforeseen challenges and ensures a smooth and efficient installation process.
Step 2: Equipment Mobilization and Setup
Once the design is finalized, the necessary equipment is mobilized to the site. This typically includes a suitable drill rig, which must be capable of delivering the required torque and thrust for the chosen anchor size and ground conditions.
Also essential are the self-drilling anchor bars, various types of sacrificial drill bits (e.g., button bits for rock, clay bits for soft ground, eccentric bits for overburden), a high-pressure grouting pump, a grout mixer, and an adequate supply of cement and additives for the grout.
Before commencing operations, the drill rig is carefully positioned and leveled at the precise anchor location, ensuring stability and accuracy throughout the drilling process. The selected drill bit is then securely attached to the leading end of the self-drilling anchor bar. All grouting lines are connected and pressure-tested, and the grout mixer is prepped to ensure immediate availability of the grout. This meticulous setup phase is crucial for operational efficiency and safety.
Step 3: Drilling and Grouting
The core of the installation process begins with the drill rig rotating and advancing the self-drilling anchor bar into the ground. The sacrificial drill bit penetrates the soil or rock, and the cuttings are expelled through the hollow core of the anchor bar or along its external flutes. Simultaneously, and often continuously, a flushing medium (such as water, air, or even grout) is introduced through the hollow bar to facilitate cutting removal and to stabilize the borehole.
For unstable or collapsing ground conditions, the “drilling-with-grout” method is often employed. In this technique, cementitious grout is continuously pumped through the hollow anchor bar as it advances.
This simultaneous grouting ensures immediate stabilization of the borehole, preventing collapse in loose soils, fractured rock, or overburden. This process creates a continuously supported and consolidated environment around the anchor, which is critical for maximizing its bond strength and pull-out capacity.
Step 4: Grout Curing and Head Installation
Once the self-drilling anchor bar has reached the designed depth and the entire bore has been filled with grout (either during drilling or as a post-drilling operation), the pumping of grout is stopped. The anchor is then left undisturbed to allow the grout to cure and gain strength.
The curing time is dependent on the type of cement used, the mix design, and ambient environmental conditions (temperature and humidity). Proper curing is essential for the grout to develop its full compressive and bond strength, which is vital for the anchor’s long-term performance and load transfer capabilities.
After the grout has achieved sufficient strength, typically verified through cube or cylinder strength tests, the anchor head is installed. This usually involves attaching a bearing plate and nut to the exposed end of the self-drilling anchor bar.
The bearing plate distributes the load from the structure or component being anchored over a wider area of the ground, while the nut secures the anchor in place. In some applications, load cells may also be installed to monitor the anchor’s performance.
Step 5: Testing and Quality Assurance
The final critical step in the installation of self-drilling anchors involves rigorous testing and comprehensive quality assurance. Load testing, such as proof testing or performance testing, is often conducted on a percentage of the installed anchors to verify their actual load-bearing capacity against the design specifications. These tests typically involve applying a predetermined tensile load to the anchor and monitoring its displacement, ensuring it meets the project’s performance criteria.
Beyond load testing, quality assurance also encompasses meticulous record-keeping, including detailed logs of drilling parameters (depth, pressure, rotation speed), grout volumes and pressures, and material certifications for the anchor bars and grout.
Post-installation inspections are also carried out to ensure the anchors are properly seated and that all components are in good condition. This comprehensive approach to testing and quality assurance guarantees the reliability and longevity of the self-drilling anchor system, providing confidence in its structural integrity.
Self Drilling Anchor Installation Considerations
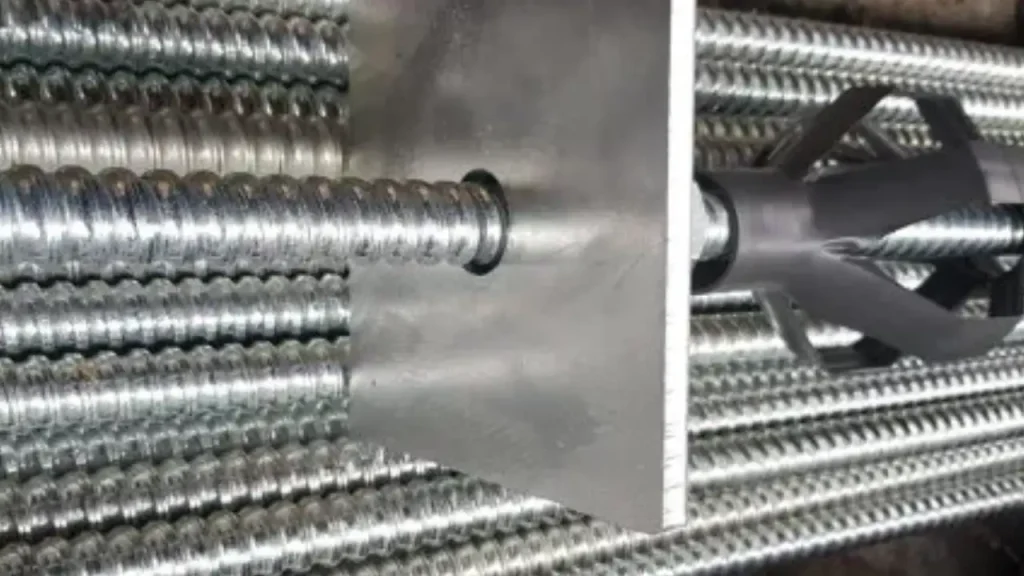

Successful self-drilling anchor installation hinges on careful planning and execution. Several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and project success.
Ground Conditions
The geological characteristics of the site are paramount. Understanding soil type, rock formations, groundwater levels, and potential obstructions is critical for selecting the appropriate anchor type, drill bit, and grouting strategy. Unforeseen ground conditions can significantly impact installation efficiency and anchor performance.
Equipment Selection
Choosing the right drill rig, grouting pump, and associated tools is vital. The equipment must be capable of handling the specific anchor size and ground conditions. Adequate power, torque, and pressure capabilities ensure efficient drilling and proper grout injection, leading to a robust anchorage.
Grouting Procedures
Proper grout mix design and injection techniques are fundamental to achieving the desired bond strength. Factors like water-cement ratio, additives, injection pressure, and curing time directly influence the anchor’s load-carrying capacity. Careful monitoring of grout volume and pressure during injection is essential for quality assurance.
Self Drilling Anchor Maintenance
Self Drilling Anchor Maintenance is essential for ensuring long-term stability, safety, and performance of anchored structures. Regular inspection and proper care prevent corrosion, loosening, and structural failures. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule extends the lifespan of anchors and ensures reliability in critical applications.
- Regular Inspection: Check anchors for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosening. Inspecting periodically ensures early detection of potential problems, allowing timely corrective action. Use visual checks and measurement tools to verify anchor integrity, preventing unexpected failures and maintaining overall safety in construction or industrial installations.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Remove debris, dirt, or rust from anchors. Applying appropriate lubricants prevents friction, wear, and corrosion. Proper cleaning improves anchor performance and ensures smooth operation during adjustments or re-tightening, protecting both the anchor and the structure it supports over time.
- Tightening and Adjustment: Periodically tighten anchors according to manufacturer specifications. Ensuring correct tension prevents movement, loosening, or misalignment. Use calibrated tools and follow recommended torque values to maintain optimal anchoring strength, extending the life and effectiveness of the installation.
- Replacement of Damaged Anchors: Replace any anchors showing significant wear, damage, or corrosion. Timely replacement prevents structural compromise and ensures safety. Using compatible, high-quality replacement anchors maintains system integrity and supports long-term stability in demanding environments.
Where to Use Self-Drilling Anchors?
Self-drilling anchors are highly versatile and widely used in various construction and geotechnical applications, especially in challenging ground conditions where traditional anchoring methods are less effective or impractical.
- Slope Stabilization: They are frequently employed to stabilize unstable slopes and embankments, preventing landslides and erosion in highway, railway, and urban development projects.
- Tunneling and Mining: In underground construction, self-drilling anchors provide essential ground support for tunnel walls and roofs, ensuring stability and safety during excavation and operation.
- Foundation Support: They are used as micropiles or tie-backs for new foundations, underpinning existing structures, and providing uplift resistance in areas with weak or variable ground.
- Retaining Walls and Excavation Support: Self-drilling anchors are crucial for anchoring retaining walls and providing temporary or permanent support for deep excavations and foundation pits, resisting lateral earth pressures.
- Bridge Construction and Rehabilitation: They offer reliable anchoring solutions for bridge abutments, piers, and other structural components, especially in challenging geological conditions.
Conclusion
Installing self-drilling anchors offers a robust and efficient solution for various construction needs, particularly in challenging ground conditions. Their integrated drilling and anchoring capability streamlines the process, saving significant time and labor on site. This method ensures a secure and reliable fix, enhancing overall project safety and durability.
The ease and effectiveness of self-drilling anchors make them an invaluable asset for modern construction. By eliminating the need for pre-drilling, they significantly accelerate project timelines and reduce operational complexities. This efficiency translates into cost savings and improved productivity for any construction endeavor.
For a reliable supply of these essential construction components, remember you can get wholesale self-drilling anchors from Sinodrills. Our products ensure high quality and performance for your projects.