We know that self-drilling anchors are essential for securing items to drywall, but sometimes they need to be removed. Whether you are redecorating a room or relocating fixtures, knowing the proper removal process is important to protect your walls. We offer these anchors for their convenience and holding power.
We provide a step-by-step guide to ensure you can remove these anchors cleanly and efficiently. Our goal is to make this task simple and damage-free so you can patch the wall and move forward with your project quickly. We use clear instructions to help you avoid unnecessary wall repair.
The Significance of Self-Drilling Anchors in Mining

Self-drilling anchors (SDAs) are vital for ground support and stability in modern mining operations. We recognize the need for rapid and reliable solutions in the challenging, dynamic environment of underground excavations. By combining drilling, grouting, and anchoring into a single step, we provide a product that significantly boosts efficiency and enhances worker safety in both tunnel and deep mine projects.
We supply SDAs to address the inherent risks of ground movement and rock falls in tunnels and stopes. Our systems ensure that immediate reinforcement is available even in unstable or fractured rock, leading to reduced downtime and a more secure worksite. We are committed to supplying tools that make ground control fast and dependable.
Applications of Self-Drilling Anchors in Mining
- Tunnel and Roof Support We offer self-drilling anchors to reinforce the roof and walls of underground tunnels and development headings. This provides immediate and long-term stability by tying unstable rock layers together, which is crucial for preventing unexpected rock falls and maintaining safe passage for personnel and equipment.
- Adaptability to Poor Ground We provide SDA systems that excel in challenging geological formations, such as fractured rock, loose soils, and water-bearing ground. Our anchors eliminate the need for pre-drilling and casing in collapsing boreholes, making the installation process faster and more reliable in otherwise difficult conditions.
- High Efficiency and Time Savings We manufacture anchors that integrate the entire installation process, saving substantial time compared to traditional bolting methods. The simultaneous drilling and grouting ensures optimal bond strength and allows miners to stabilize ground and advance the excavation more quickly and cost-effectively, increasing overall productivity.
- Safety in Emergency Reinforcement We supply anchors for rapid response situations, such as stabilizing mine shafts, highwalls in open-pit mines, or rescue routes. Their quick installation capability allows for immediate support in areas where ground conditions change suddenly, providing a secure working area with minimal exposure to unsupported rock.
Reasons for Removing Self-Drilling Anchors
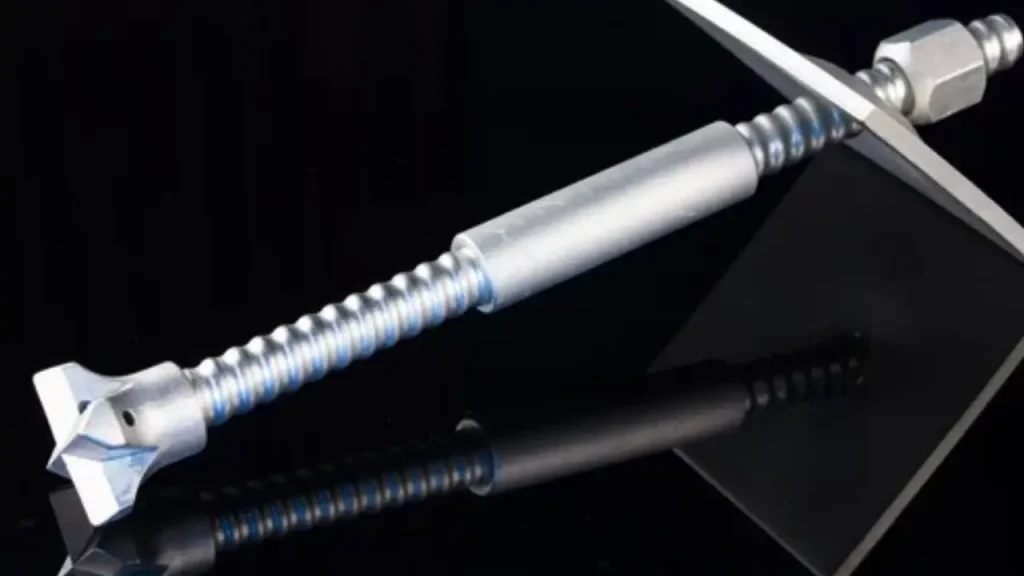

We recognize that removing existing self-drilling anchors is often a necessary preliminary step before commencing heavy or specialized drilling work. When you are installing new equipment or undertaking structural reinforcement, we advise clearing the area of old fixings. This ensures the integrity of the new installation and prevents complications with the larger, heavier drills you plan to use.
We recommend anchor removal to guarantee a clean substrate that is free from obstructions. This practice is critical for maintaining the precision and performance of your heavy drilling equipment, whether for large-diameter holes or for installing high-capacity anchoring systems. We help you establish the best foundation for your next major project.
Key Reasons for Removing Self-Drilling Anchors
Risk of Tool Damage
We advise removing older anchors because drilling directly into existing metal or plastic components can severely damage expensive drill bits or impact the hammer drill mechanism. Clearing the anchors prevents bit binding, breakage, or deflection, ensuring your heavy-duty tools remain sharp and operational for their intended task.
Compromised Substrate Integrity
We know that previous anchor holes can leave the base material weaker than virgin material. Heavy drilling near old anchors, especially in drywall or masonry, can cause unexpected breakout or crumbling. We recommend removal and proper patching to restore the wall’s structural soundness before installing new, heavier fixings.
Obstruction of New Anchor Placement
We find that old anchors can occupy the precise space needed for a new, higher-capacity anchor (like a heavy-duty sleeve or wedge anchor). Removing the old fixing ensures the new bore hole is positioned accurately and is clean, which is essential for achieving the maximum load-bearing capacity for the subsequent heavy installation.
Preventing Bit Deflection and Misalignment
We understand that heavy drilling requires absolute precision. An existing, non-removed self-drilling anchor can cause the new, larger drill bit to deviate from its intended path, resulting in a misaligned or oversized hole. We prioritize removing them to maintain the tight tolerances required for structural applications.
How to Remove Self-Drilling Anchors
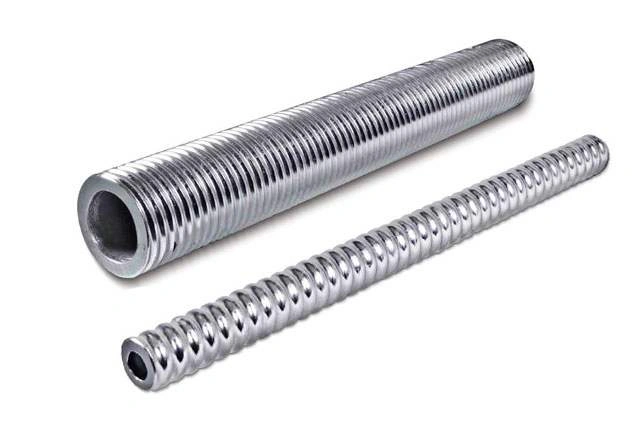

We know that in the rock drilling industry, especially when dealing with temporary ground support, the removal of self-drilling anchors (SDAs) is sometimes necessary before blasting or new installations. While designed for permanent stability, certain circumstances require their extraction to clear the working face or recover materials. We provide procedures that minimize damage to the rock structure.
We supply methods that help you manage the removal process, particularly when utilizing SDAs for applications like pre-support or stabilization of initial excavation. Our guidance focuses on techniques that are safe, efficient, and appropriate for the heavy machinery and demanding conditions found in a mine or tunnel environment. We prioritize quick operational turnover.
Tools Needed
- Extraction tool (e.g., specialized hydraulic jack or manual puller)
- Cutting torch or specialized diamond saw (if anchor must be cut)
- Shovel and bucket (for clearing grout/debris)
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Step 1: Preparation and Safety Check
We emphasize a thorough safety assessment of the rock face before any removal attempt. We need to ensure the immediate surrounding rock mass is stable and that no residual load is present on the anchor system. We secure the area to protect workers from potential rock falls or shifting ground during the operation.
We provide a system for clearing all surface debris and residual grout around the anchor head, ensuring a clean working area. This preparation allows for the secure seating of the extraction tool or cutting equipment. We make sure that all personnel are aware of the procedure and safety protocols.
Step 2: Unloading and Cutting the Anchor
We recommend using a specialized hydraulic jack or puller to apply a controlled tension force to the anchor bar. This process effectively unloads any remaining residual tension within the anchor system, making it safe for the next step. We manufacture tools designed to handle the high forces associated with rock support elements.
We supply cutting equipment, such as a torch or saw, to efficiently sever the exposed part of the anchor bar near the rock surface. We ensure the cut is flush or slightly recessed into the rock face to eliminate any protrusions that could interfere with subsequent drilling or blasting operations.
Step 3: Extracting the Bar and Grout
We find that once the anchor is unloaded and cut, the exposed bar and residual grout can often be removed using a reverse hammering action or a mechanical puller. We recommend applying gradual force to pull the rod out of the bore, minimizing potential damage to the surrounding rock structure.
We advise clearing the borehole completely of all foreign material, including any remaining grout or rock fragments. We ensure the hole is fully cleaned and ready, which is crucial if the location is to be used immediately for a new, heavier anchor system or before any blasting takes place.
Safety Considerations about Removing Self Drilling Anchors

We consider safety as the highest priority when undertaking any task in the drilling or construction industry, especially when removing self-drilling anchors (SDAs). We stress that even seemingly small tasks carry risks that must be managed through strict adherence to safety protocols and proper planning. We aim to protect personnel and prevent damage to the surrounding structure during the removal process.
We advise that before starting the extraction process, a comprehensive site-specific risk assessment must be completed. This includes identifying potential hazards like unstable rock, residual tension in the anchors, or the presence of underground utilities. We provide training materials to ensure every worker understands the proper use of removal tools.
⚠️ Safety Considerations for SDA Removal
Proper Tool Operation and Training
We stress that only trained personnel should operate specialized removal tools, such as hydraulic pullers or cutting torches. We provide clear operating procedures for all our equipment to prevent tool failure or accidental misuse. We manufacture our tools to the highest standards of safety and durability.
Rock Mass Stability Assessment
We require a thorough check of the immediate rock or substrate surrounding the anchor to ensure it remains stable after the anchor is unloaded. Removing ground support can introduce risks of local rock falls or loosening of the face. We provide guidelines for re-supporting critical zones before anchor extraction begins.
Managing Residual Anchor Load
We emphasize the danger of uncontrolled energy release if the anchor is still under tension. We recommend using a controlled de-tensioning tool to safely relieve any residual load before cutting or extracting the bar. This action prevents the anchor bar from whipping or snapping upon removal, protecting nearby workers.
Use of Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
We mandate the use of heavy-duty gloves, safety glasses, and hard hats during all anchor removal activities. We know that flying debris, sharp edges from a cut bar, or falling rock fragments are potential hazards. We supply high-visibility clothing to enhance worker safety in busy construction or mining areas.
Conclusion
Successfully removing your self-drilling anchors allows you to patch and refinish your wall with minimal effort. We understand that flexibility and ease-of-use are key for all your projects. By following our guide, you can confidently take down old fixtures and prepare your space for its next look. We always focus on supplying reliable and user-friendly products for professional results.
If your project involves new installations, we encourage you to purchase replacement self-drilling anchors directly from Sinodrills. We manufacture an extensive range of anchors known for their exceptional strength and easy installation. Our wholesale pricing ensures you get the best value without compromising on the holding capacity and durability required for heavy-duty applications.
Ready to restock your inventory with premium fastening solutions? We supply Sinodrills’ self-drilling anchors in bulk quantities to support your business needs effectively. Contact us today to learn more about our wholesale program and how we can provide the high-performance anchors that your customers demand.