Custom PDC Bit Dull Grading Manufacturer in China
Optimize your drilling performance with our expert PDC bit dull grading services. We provide precise analysis of wear patterns, cutter damage, and overall bit condition, enabling informed decisions for bit selection and operational adjustments. Maximize bit lifespan, enhance drilling efficiency, and reduce costs with our comprehensive dull grading solutions.
Customize Your Desired Dull Grading PDC Bit
Get precise, tailored PDC bit dull grading to meet your specific needs. We customize our analysis to focus on the wear characteristics most critical to your operations, from cutter degradation to gauge wear. This targeted approach delivers actionable insights, empowering you to optimize bit design, maximize drilling efficiency, and significantly reduce costs.
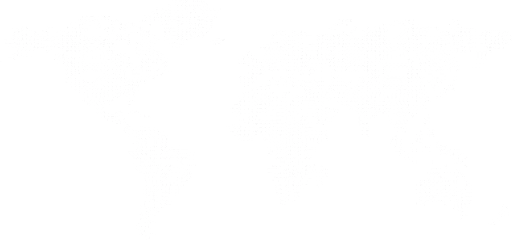
DPC Bit inner & outer row
Our PDC bit dull grading meticulously assesses both inner and outer row cutter wear. We calculate and record the average wear for each, providing clear metrics. Importantly, gauge cutters are explicitly excluded from the outer row wear calculation to ensure accurate analysis of the primary cutting structure’s performance. This detailed approach optimizes bit selection and maximizes drilling efficiency.
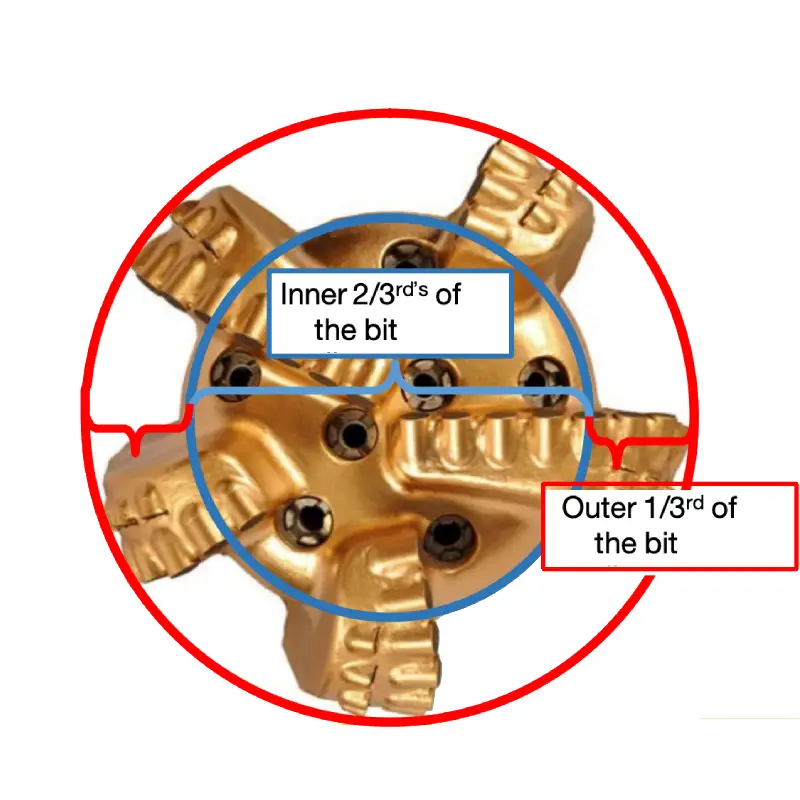
DPC Bit inner & outer row Location
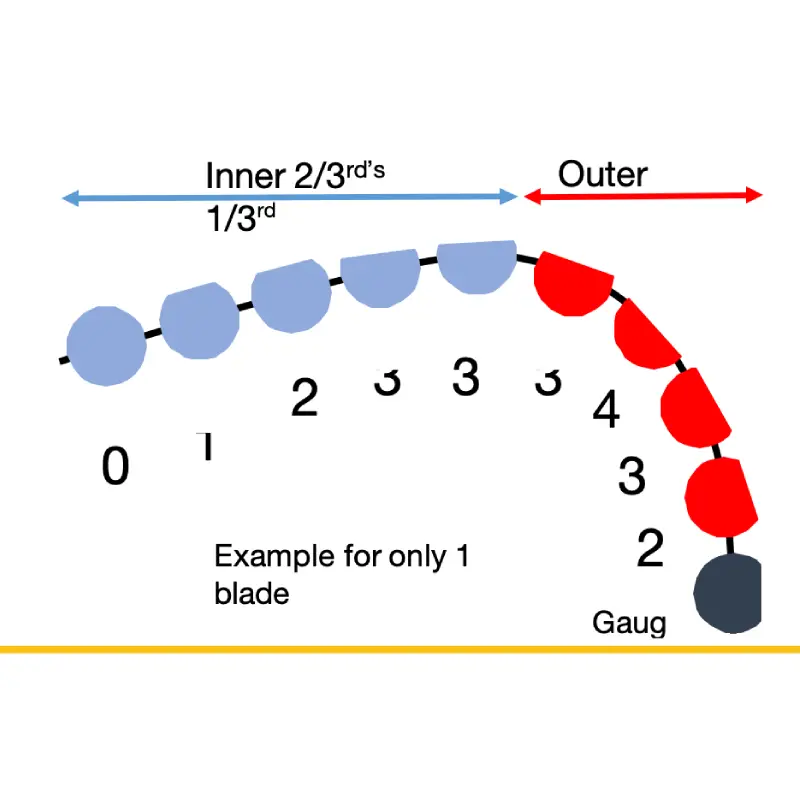
Our PDC bit dull grading precisely defines inner and outer row wear. The highest cutter on each blade marks the approximate transition between the Inner 2/3rds and Outer 1/3rd of the bit face. This clear distinction allows for accurate measurement of wear patterns in both critical regions, optimizing bit performance analysis.
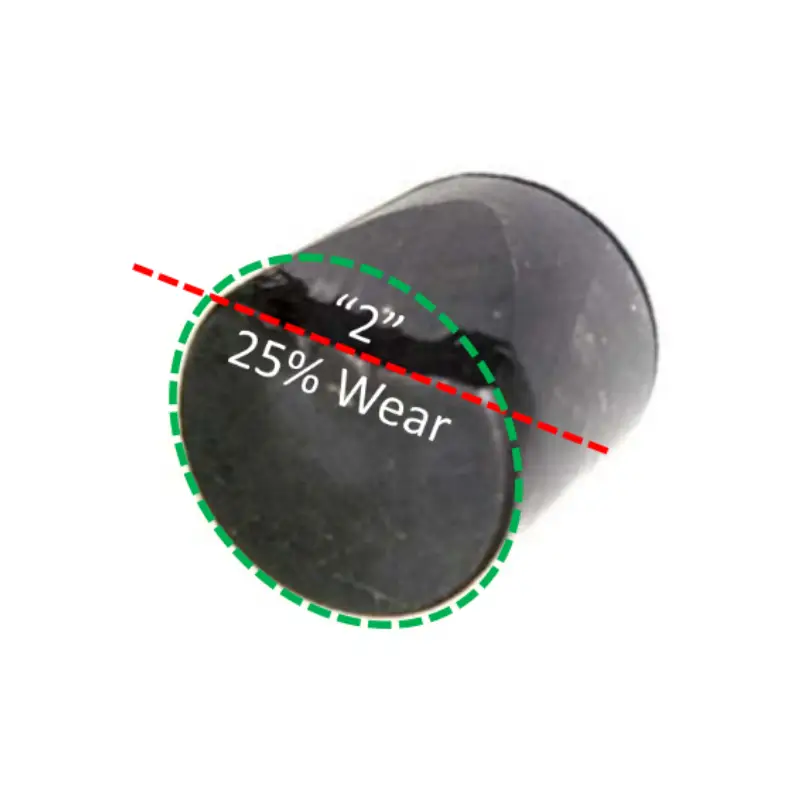
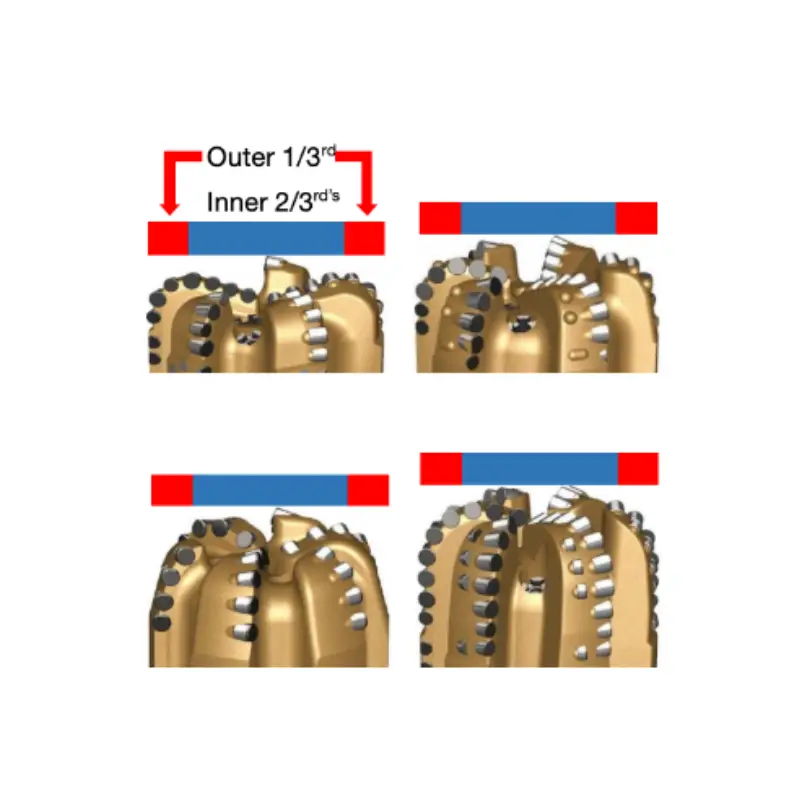

DPC Bit cutter wear
Our PDC bit dull grading precisely quantifies cutter wear to optimize future drilling. “25% Wear” on the cutter corresponds to a “2” on the 0-8 dull grading scale, indicating 2/8ths of the diamond layer is worn. This standardized measurement across the diamond table allows for consistent evaluation, informing decisions to maximize bit life and drilling efficiency.
Calculating Average Cutter Wear for Inner & Outer Rows
To accurately assess the wear on PDC bits, the average cutter wear for both inner and outer rows is calculated using a specific methodology. This process ensures a consistent and standardized evaluation of the bit’s cutting structure.
Here are the steps involved in calculating average cutter wear:
- Grade each cutter: Assign a wear grade from 0 to 8 to each individual cutter.
- Sum the values: Add up the wear grades for all cutters within the specific row (inner or outer).
- Divide by the number of cutters: Divide the total sum by the number of cutters in that row to get the average.
- Round to the nearest number: Round the calculated average to the nearest whole number to determine the final average wear grade.
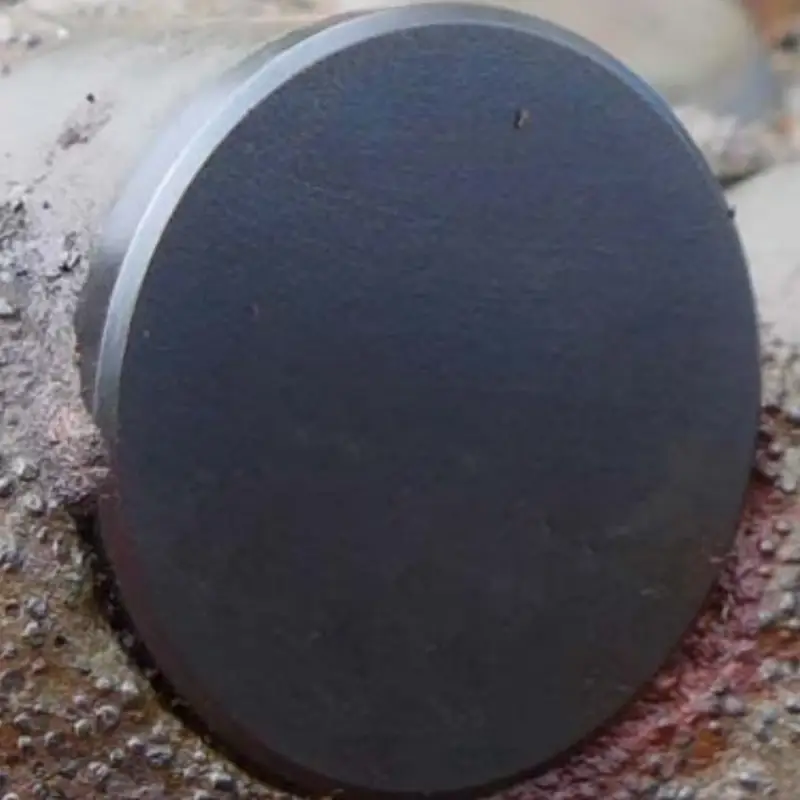

DPC Bit cutters
PDC drill bit cutters feature a diamond table where wear is measured, impacting drilling efficiency. Dull grading assesses various damage, including chipping, breakage, and material loss from the diamond table. Accurate evaluation of these cutters, including specific wear patterns like flat-crested wear or heat checking, is crucial for optimizing bit performance and future bit selection.
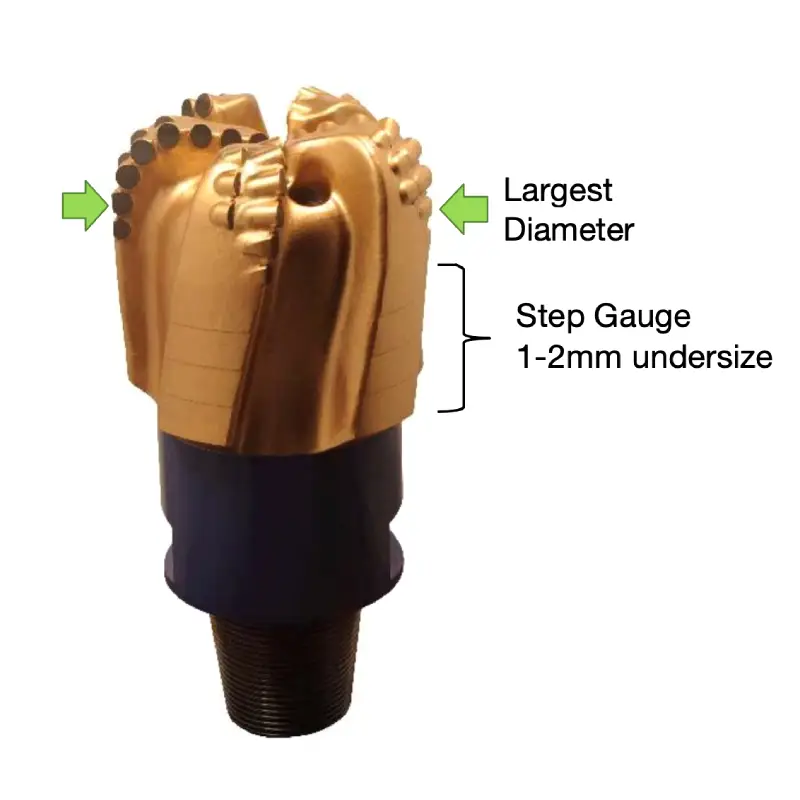
PDC bit Gauge Sizes
Customize your PDC bit gauge sizes for optimal drilling performance. We tailor gauge dimensions to counter wear, prevent undersized holes, and maintain stability. Precision customization, factoring in pre-ground gauge cutters and varying grind amounts by product line, ensures your bit remains in-gauge longer, maximizing efficiency and minimizing costly reaming operations.


DPC Bit cutters
A PDC drill bit body serves as the foundation for the bit’s cutting structure, housing the PDC cutters and various other components essential for drilling performance. Its design is crucial for stability, hydraulic efficiency, and durability in downhole conditions.
Matrix Body: These are typically manufactured from tungsten carbide powder infiltrated with a molten binder alloy. This process results in a very robust, erosion-resistant body ideal for abrasive formations and minimizing washouts.
Steel Body: Constructed from high-strength alloy steel, these bodies are often more ductile and repairable. Steel bodies allow for larger junk slots and can be more economical, though they may require more protection in highly abrasive environments.
Junk Slots/Blades: These are channels and extended structures on the bit body that facilitate the flow of drilling fluid and cuttings away from the bit face, preventing balling and ensuring efficient drilling.
Nozzles: Ports within the bit body through which drilling fluid is directed to clean the cutters and cool the bit, as well as to lift cuttings from the wellbore.
PDC bit Dull Grades
IADC 8-Box System: The International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC) uses an eight-box system to capture the dull bit condition and the reason it was pulled from the hole.
Cutter Wear (Inner & Outer Rows): The average wear of cutters in both the inner two-thirds and outer one-third of the bit face is calculated and graded on a scale of 0-8, where 0 is no wear and 8 is 100% wear. Gauge cutters are excluded from the outer row wear calculation.
Primary Dull Characteristic: The most prominent physical change from the new condition of the cutter is recorded. This can include issues like bond failure, broken cutters, chipping, erosion, heat checking, or lost cutters.
Location of Primary Dull: Indicates where the primary dull characteristic is located on the bit, such as the cone, nose, shoulder, taper, or gauge.
Bearing & Seals: For fixed cutter bits, this box is typically marked “X” as it’s primarily used for roller cone bits.
Gauge Undersize: Records the condition of the bit’s gauge, noting if it’s “In-Gauge” (I) or how much it is undersized in 16ths of an inch.
Other Dull Characteristics: Documents secondary evidence of bit wear or damage to the bit as a whole, such as bit body erosion, junk damage, or plugged nozzles.
Reason Pulled: States the reason the bit was removed from the well, which could range from reaching total depth to downhole motor failure or hole problems

Customize Your Desired PDC Bit Dull Grading
Tailored Inner & Outer Row Analysis
We meticulously analyze wear patterns on both inner and outer rows, providing distinct measurements. This allows us to customize the focus of our reports to highlight specific wear trends relevant to your drilling conditions, ensuring you get actionable insights for optimizing bit selection and design for maximum efficiency.
Precise Cutter Wear Quantification
We employ a precise 0-8 scale to quantify individual cutter wear, translating to the exact percentage of diamond layer worn. This granular detail enables us to customize our recommendations for cutter material and placement, directly addressing the abrasive or impact challenges faced, thereby extending bit life and enhancing penetration rates.
Detailed Gauge Size Assessment
We provide a thorough assessment of the bit’s gauge condition, indicating if it’s in-gauge or undersized in 16ths of an inch. We customize this data to show critical gauge wear trends, helping you make informed decisions about when to pull the bit and prevent costly reaming, ensuring accurate hole sizes.
Focused Primary Dull Characteristic Identification
We prioritize identifying the primary dull characteristic that most influenced the bit’s performance or required it to be pulled. Our customization focuses on this key finding, allowing us to deliver targeted recommendations for operational adjustments, or future bit designs, ultimately improving overall drilling economics.
what is a PDC bit?
A Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) bit is a type of drill bit used in drilling operations, particularly in the oil and gas industry.
It features synthetic diamond cutters that are fused onto a tungsten carbide substrate, providing exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance. These bits are highly effective for drilling through various rock formations, offering faster penetration rates and longer tool life compared to conventional roller cone bits, thereby improving overall drilling efficiency.
pDC bit dull grading chart
” Dull Grading for PDC Drill Bits,” outlines the system used to grade the condition of PDC drill bits after use. It details an 8-box system to capture the dull bit condition and the reason it was pulled.
Here is the PDC bit dull grading chart, often referred to as the IADC (International Association of Drilling Contractors) dull grading system:
Dull Grading – 8 Boxes
Inner Rows (Average Cutter Wear): Records the average wear of cutters in the inner 2/3rds of the bit diameter. A grading scale of 0-8 is used, where 0 indicates 0% wear and 8 indicates 100% wear (8/8ths).
Outer Rows (Average Cutter Wear): Records the average wear of cutters in the outer 1/3rd of the bit diameter. This also uses a 0-8 scale. Gauge cutters are excluded from this calculation.
Primary Dull Characteristic: Describes the most prominent physical change from new condition of the cutter.
Examples include:
- BF: Bond Failure
- BT: Broken Cutter
- CT: Chipped Cutter
- ER: Erosion
- FC: Flat Crested Wear
- HC: Heat Checking
- LT: Lost Cutter
- NO: No Characteristics
- RG: Rounded Gauge
- WT: Worn Cutters
Location of Primary Dull Characteristic: Indicates where the primary dull characteristic is located. Codes include:
- C: Cone
- N: Nose
- S: Shoulder
- T: Taper
- G: Gauge
- A: All
Bearing & Seals: For fixed cutter bits (PDC bits), this box is always marked “X” as it is primarily used for roller cone bits.
Undersize (16ths inch): Records the condition of the bit gauge. “I” is used for a bit that is still in gauge, otherwise, the amount the bit is under gauge is recorded to the nearest 1/16th of an inch (e.g., “1” for 1/16th undersize, “2” for 2/16ths undersize).
Other Dull Characteristic: Notes secondary evidence of bit wear, which can relate to cutting structure wear or overall bit wear. This box can also describe other bit components like hydraulics or general condition.
Reason Pulled: Explains why the bit was pulled out of the hole.
Examples include:
- BHA: Changed Bottom Hole Assembly
- DMF: Downhole Motor Failure
- DSF: Drill String Failure
- FM: Formation Change
- HP: Hole Problems
- PR: Penetration Rate
- TD: Total Depth
what are PDC bits used for?
PDC bits are primarily used for drilling in a variety of challenging geological formations due to their exceptional cutting efficiency and durability. Their common applications include:
Oil and Gas Drilling: They are extensively used to drill through diverse rock types, from soft shales to hard, abrasive sandstones, in both vertical and horizontal wells.
Geothermal Drilling: PDC bits are effective in high-temperature environments encountered during geothermal well construction.
Mining: They find application in drilling blast holes and exploration bores.
Water Well Drilling: For efficient and rapid drilling of water wells, especially in areas with consolidated formations.
why choose our PDC bits?
Choosing our PDC bits provides a distinct advantage in your drilling operations due to their superior design and performance capabilities. We engineer our bits for:
Exceptional Durability: Our PDC bits are crafted with premium synthetic diamonds and advanced bonding technologies, ensuring extended tool life even in the most abrasive formations.
Optimized Penetration Rates: The innovative cutter layouts and hydraulic designs facilitate aggressive cutting and efficient chip removal, leading to faster drilling and reduced rig time.
Reduced Operational Costs: By maximizing bit life and improving ROP, our bits minimize the need for frequent bit changes, significantly lowering your overall drilling expenses and increasing project profitability.
Versatile Application: Designed to perform across a wide range of rock types and drilling environments, our PDC bits offer reliable and consistent performance for diverse project requirements.
how to use PDC bits?
PDC bits are highly effective tools for optimizing drilling operations. Understanding their proper usage is essential for maximizing efficiency, extending bit life, and ensuring successful penetration through various formations.
Step 1: Bit Selection
Choosing the appropriate PDC bit design is crucial. Consider the rock formation, desired rate of penetration, and well trajectory. Selecting the right cutter density and blade count ensures optimal performance and minimizes bit wear in specific drilling environments.
Step 2: Drilling Parameters Optimization
Maintaining optimal drilling parameters is vital. Adjust weight on bit (WOB) and rotary speed (RPM) based on real-time feedback. Proper hydraulics and flow rates are necessary to efficiently clean the cutters and remove cuttings from the wellbore.
Step 3: Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuously monitor bit performance and downhole conditions. Early detection of vibration or torque fluctuations helps prevent damage. Regular inspection during trips ensures the bit remains in good condition, allowing for informed decisions on dull grading.
Send Your Inquiry Now
All-in-one PDC Bit Dull Grading Solutions for Your Project
Uncertainty in PDC bit performance leads to costly downtime and inefficient drilling. Our all-in-one PDC bit dull grading solutions eliminate guesswork, transforming your challenges into precise, actionable insights. We provide comprehensive analysis of every bit, guiding optimal selection and operational adjustments. Maximize bit life, enhance drilling efficiency, and significantly reduce project costs, ensuring superior performance and profitability for your drilling endeavors.