Soil nailing is a widely used technique in geotechnical engineering to reinforce slopes and excavations. By inserting steel bars into the soil, it improves stability and prevents erosion or collapse. Understanding the different types of soil nailing is essential for selecting the right method for each construction scenario.
Different soil conditions and project requirements dictate the choice of soil nailing systems. Some types are better suited for temporary stabilization, while others provide long-term structural support. Exploring their applications helps engineers and contractors optimize safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in retaining walls, slopes, and excavation projects.
What is Soil Nailing
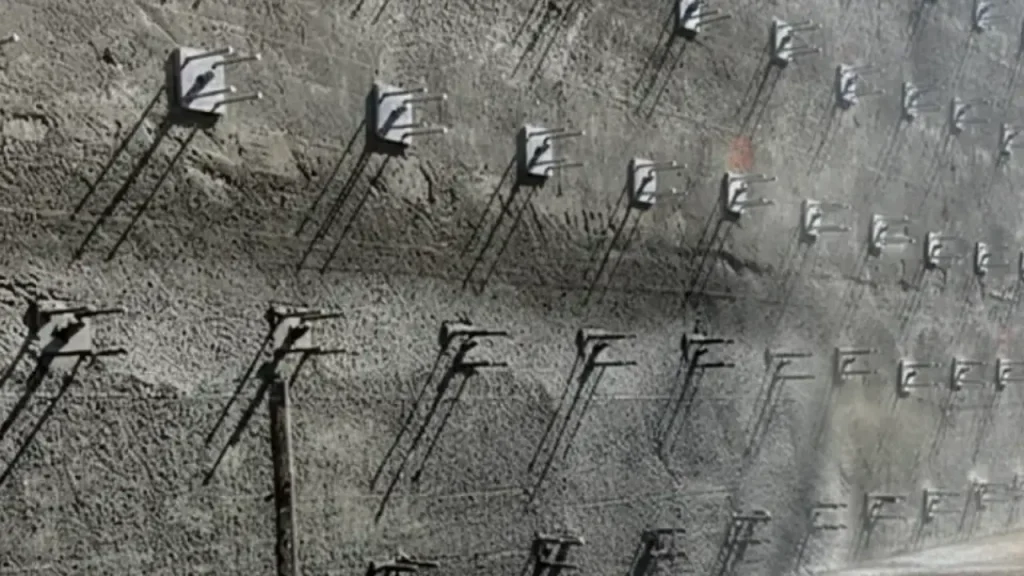

Soil nailing is a ground reinforcement technique used in construction to stabilize slopes, excavations, and retaining walls. It involves inserting steel bars, called nails, into the soil and securing them with grout.
This method strengthens weak soil, prevents erosion or collapse, and enhances structural stability. It is effective, cost-efficient, and widely applied in geotechnical engineering projects.
Types of Soil Nailing
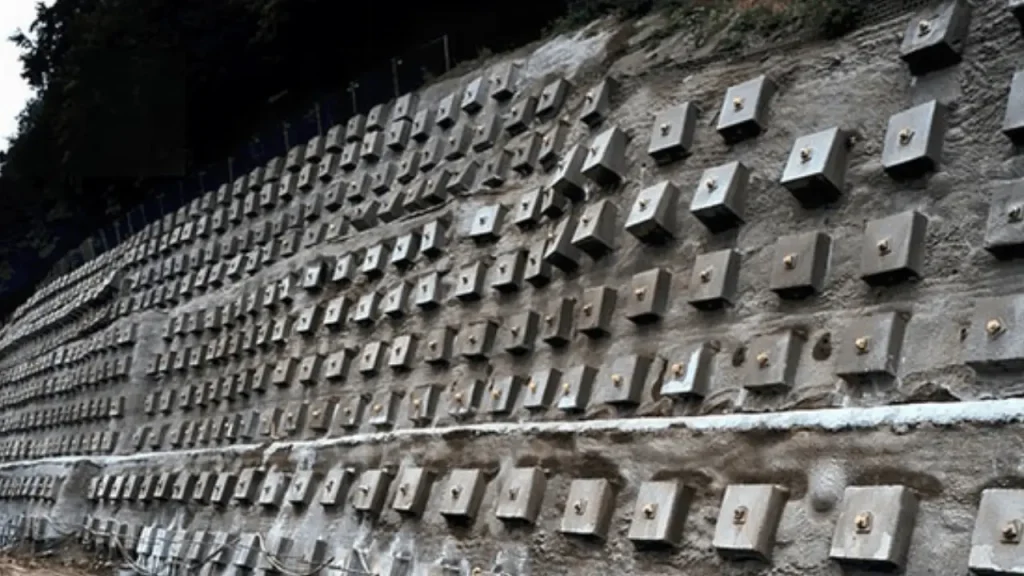

Soil nailing is a versatile technique used to reinforce slopes, excavations, and retaining walls. Different types of soil nailing offer unique methods and benefits, tailored to specific soil conditions and project needs.
Understanding these types helps engineers select the most effective solution for stability, safety, and long-term performance.
Conventional Soil Nailing
Conventional soil nailing is the most commonly used method, involving pre-drilled holes where steel bars are inserted and grouted. It is ideal for slopes and excavations with moderate soil stability, providing reliable support and easy installation for small to medium-scale projects. This technique strengthens the soil by creating a reinforced mass that resists movement.
This method allows flexibility in nail spacing, length, and inclination, adapting to varying site conditions. Engineers can optimize design based on soil type and load requirements, ensuring effective stabilization. Maintenance is minimal, and the system integrates well with other retaining structures, making it a practical choice for long-term slope reinforcement.
Mechanically Anchored Soil Nailing
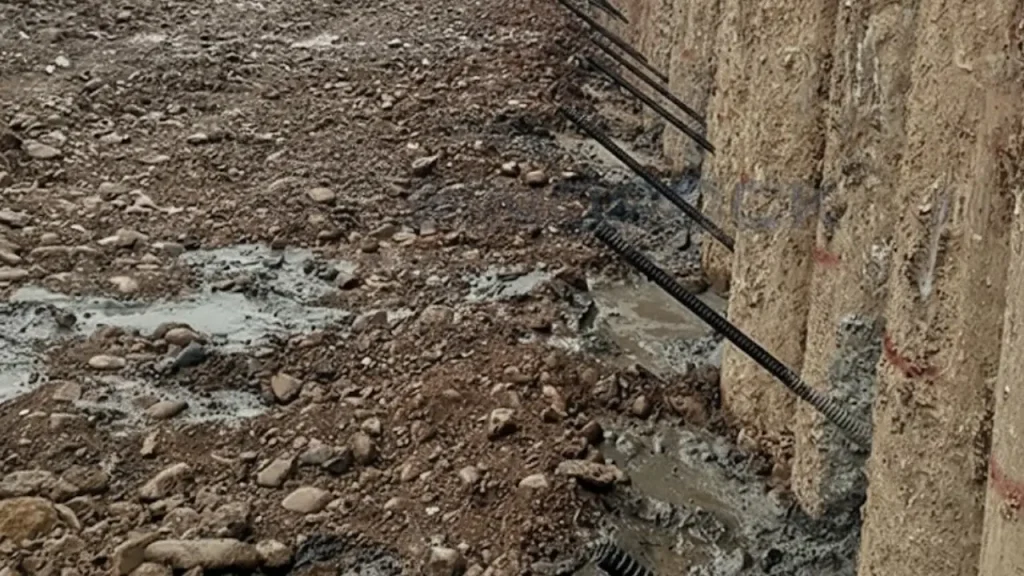

Mechanically anchored soil nailing uses bars with specialized self drilling anchors or plates to enhance soil grip without relying solely on grout. This type is suited for loose or highly fractured soils where conventional nailing might not provide enough stability. It increases resistance to soil movement and distributes loads more efficiently.
Installation involves inserting bars into drilled holes and securing the mechanical anchors against soil layers. This method reduces reliance on grout strength and allows quicker load transfer, making it suitable for projects requiring rapid stabilization. It also improves safety in steep or unstable terrain, providing additional assurance against soil failure.
Driven Soil Nailing
Driven soil nailing installs steel bars directly into the ground using impact or vibration, eliminating the need for extensive drilling. This method is fast and cost-effective, especially in cohesive soils or urban areas where minimal disturbance is desired. It reduces installation time while maintaining strong soil reinforcement.
Driven nails can be combined with grouting or left ungrouted depending on project requirements. The technique is efficient for temporary or permanent support and works well for shallow slopes or excavation faces. It is also adaptable to varying soil conditions, providing a practical solution for tight construction schedules.
| Type of Soil Nailing | Installation Method | Best Use Case | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Soil Nailing | Drilled holes, steel bars, grouted | Moderate slopes and excavations | Flexible design, reliable, low maintenance | Slower for large projects |
| Mechanically Anchored Soil Nailing | Steel bars with anchors or plates | Loose or fractured soils | Quick load transfer, high stability | Requires specialized anchors |
| Driven Soil Nailing | Direct insertion, impact or vibration | Shallow slopes, urban areas | Fast, cost-effective, minimal disturbance | Limited depth, soil type dependent |
How to Choose Suitable Soil Nailing?
Choosing the right soil nailing system is essential for ensuring slope stability and structural safety. Factors such as soil type, slope height, load requirements, and project duration influence the selection. Proper evaluation ensures effective reinforcement, reduces construction risks, and enhances long-term durability for excavations, retaining walls, and other geotechnical projects.
- Assess Soil Conditions: Understanding soil composition, cohesion, and moisture content is crucial. We analyze these factors to determine nail type, length, and spacing. Proper assessment prevents failure, ensures load distribution, and guides installation techniques, providing a stable and reliable reinforced soil structure for construction projects.
- Determine Project Requirements: Consider slope height, excavation depth, and expected loads. We evaluate project specifications to select a soil nailing method that balances strength, efficiency, and cost. This approach ensures optimal reinforcement tailored to site conditions while minimizing material waste and construction delays.
- Choose Appropriate Nail Type: Different soil nailing types offer distinct benefits. We select nails based on mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and installation method. This choice enhances structural integrity, adapts to challenging soil conditions, and ensures the reinforcement system performs reliably over the project’s lifetime.
- Evaluate Installation Techniques: Installation method affects cost, speed, and effectiveness. We plan drilling, grouting, or driving techniques based on site constraints. Efficient installation reduces labor, minimizes soil disturbance, and ensures nails achieve their intended load-bearing capacity, improving overall project safety.
- Consider Long-Term Maintenance: Soil nailing systems require minimal upkeep if designed properly. We factor in durability, environmental conditions, and potential erosion. Choosing the right system reduces maintenance costs, extends lifespan, and ensures the reinforced soil continues to provide reliable stability throughout the structure’s service period.
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate soil nailing type ensures stability, safety, and longevity for construction projects. Each system offers distinct advantages based on soil conditions, load requirements, and project goals. Proper selection minimizes risks and maintenance while improving structural performance. For reliable materials, get wholesale self-drilling anchor systems from Sinodrills.
Understanding soil nailing techniques also helps streamline project planning and execution. Contractors can select methods that match site-specific challenges, reducing delays and unexpected costs. Using professional-grade systems like Sinodrills’ self-drilling anchors ensures high performance, durability, and efficiency for both temporary and permanent soil stabilization needs.
By mastering the differences and applications of soil nailing, engineers can enhance slope and excavation safety. Efficient implementation improves structural integrity and supports long-term project success. For trusted wholesale solutions, Sinodrills offers self-drilling anchor systems that meet rigorous standards and provide reliable results for any geotechnical project.