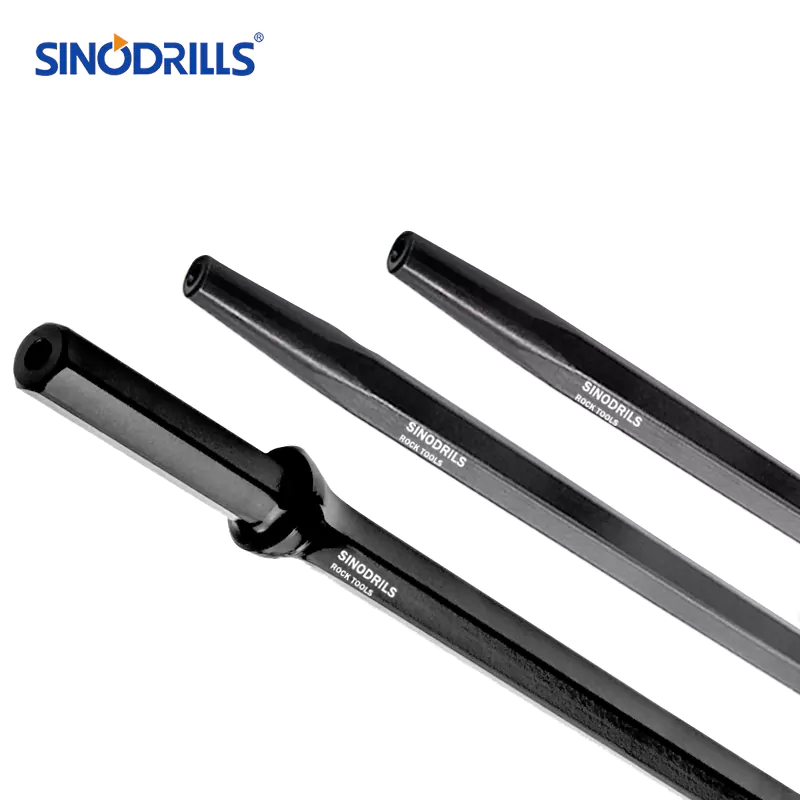
Drill rods are fundamental tools in numerous industries, but their diverse applications necessitate a range of specialized types. Understanding the distinctions between these rods is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring success in various drilling operations.
This guide will delve into the different categories of drill rods, highlighting their unique characteristics and intended uses. From water well drilling to mining and directional boring, we’ll explore how each type is engineered for specific challenges and environments.
What are Drill Rods?
Recommended Drill Rods
Drill rods are precision-engineered metal bars, typically made from high-quality alloy steels, designed for demanding industrial applications. While used in drilling, their precise dimensions and robust material properties also make them ideal for crafting various tools, machine components, and specialized parts requiring high strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Types of Drill Rods
Drill rods come in various types, each designed to meet the specific demands of different drilling methods and applications. These distinctions are often based on the connection type, body shape, or the drilling system they are a part of, each optimized for performance and durability under unique conditions.
The choice of drill rod is critical for maximizing efficiency, ensuring hole accuracy, and preventing premature equipment failure. Here are the primary categories of drill rods and their distinct characteristics.
Based on Connection Type
Extension Drill Rods (MM)
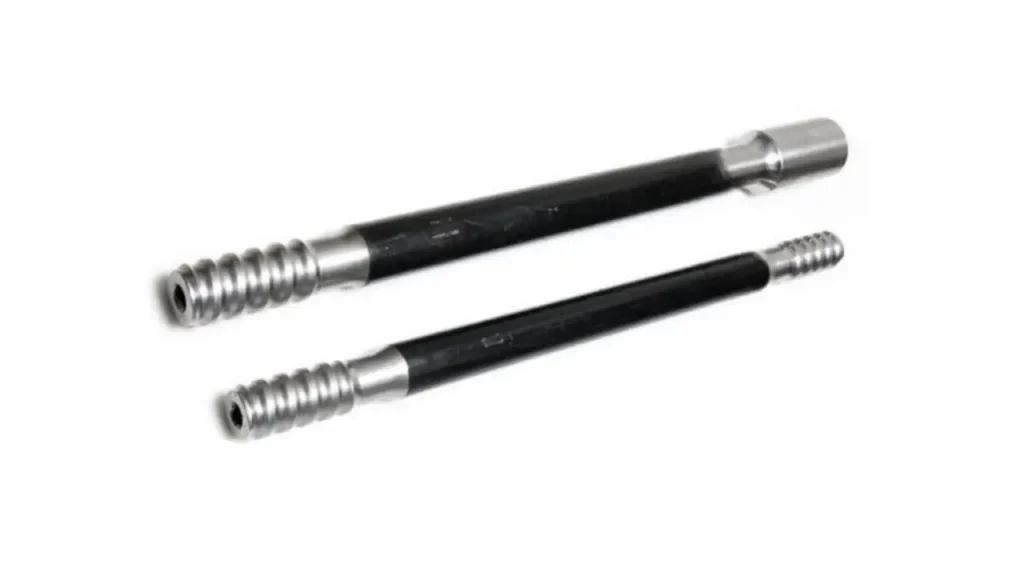

Extension drill rods, also known as Male-Male (MM) rods, have external threads on both ends. They are the most traditional type of drill rod and are connected using a separate threaded coupling. This design allows for a modular drill string that can be easily extended with additional rods and couplings. Extension rods are highly versatile and are widely used in tunneling, mining, and quarrying for a range of drilling depths.
While this system is adaptable, the use of a separate coupling can introduce a point of weakness and a source of energy loss. The coupling and rod threads must be carefully maintained to prevent wear and ensure a strong, reliable connection. This style is often used with a variety of thread types to match different shanks and bits.
MF Drill Rods (Male-Female)
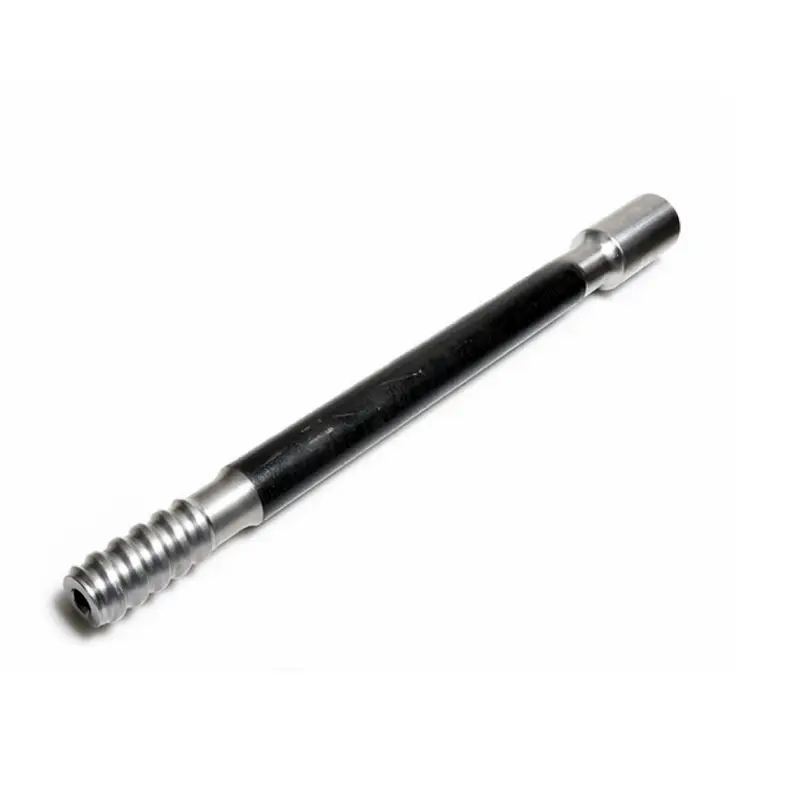


MF drill rods feature an integrated connection, with a male thread on one end and a female thread on the other. This design eliminates the need for a separate coupling, creating a more rigid and streamlined drill string. The single-piece connection improves energy transfer from the drifter to the bit, leading to faster penetration rates and better hole straightness.
MF rods are particularly beneficial for long-hole drilling where hole deviation is a concern. The simpler connection process reduces the time required for rod changes, boosting overall productivity and reducing physical strain on the operator. This design also reduces inventory, as couplings are not needed, and minimizes a common failure point.
Based on Body Type

Round Drill Rods
Round drill rods have a circular cross-section, a design that is both simple and highly effective for general-purpose drilling. This body type provides a balance of strength and flexibility, making it a reliable choice for a wide variety of rock formations. The smooth profile of the rod body allows for efficient rotation and easy handling, which is advantageous in many drilling scenarios.
Round rods are a cost-effective option and are widely compatible with standard drilling equipment. While they are suitable for most applications, their design can sometimes lead to reduced flushing efficiency in certain ground conditions compared to hexagonal rods, as the smooth surface provides less turbulence for the flushing medium.
Hexagonal Drill Rods
Hexagonal drill rods are characterized by their six-sided cross-section. This body type is engineered for enhanced rigidity and improved flushing capabilities. The flat sides of the rod create a larger and more defined channel for the air or water flushing medium to pass through, which is particularly effective in removing cuttings from the borehole.
The added rigidity of hexagonal rods helps to maintain better hole straightness and withstands higher bending stress, making them ideal for demanding applications. They are often the preferred choice in drifting and tunneling where precise hole alignment and efficient debris removal are critical for the success of the operation.
Based on the Drilling Method

Top Hammer Drill Rods
Top hammer drill rods are used in percussive drilling, where a drifter mounted on the top of the drill rig delivers both a powerful hammer action and rotational force. These rods are typically extension rods or MF rods, designed to withstand the immense impact energy from the piston. The rods’ primary function is to efficiently transmit this energy to the bit.
The material and heat treatment of top hammer rods are critical to their performance, as they must endure constant shock loading and torsional stress. They are a staple in mining, quarrying, and construction for drilling blast holes and rock anchors, and are optimized for fast penetration in hard rock formations.
DTH (Down-the-Hole) Drill Rods
DTH drill rods are used in down-the-hole drilling, where a pneumatic or hydraulic hammer is located at the bottom of the drill string, right behind the drill bit. Unlike top hammer rods, DTH rods do not transmit the percussive energy. Instead, their main role is to rotate the hammer, provide feed force, and channel high-pressure air to operate the hammer and flush cuttings.
These rods are typically larger in diameter than top hammer rods and are designed for a different set of stresses. Their primary requirements are high rotational strength and the ability to handle the internal air pressure. DTH drilling is favored for very deep holes and in fractured or soft ground where a stable, straight hole is needed.
Based on Application
Tapered Drill Rods
Tapered drill rods are used in light-duty percussive drilling, often with handheld rock drills or small, pneumatic drill rigs. These rods feature a forged, tapered end that fits into a corresponding tapered hole in the drill bit. This connection is maintained by the impact energy of the drill, which wedges the bit onto the rod. No threads are used for the connection between the rod and the bit.
The simplicity of the tapered connection makes it easy to set up and disconnect, which is ideal for small-scale projects. Tapered rods are typically shorter than extension rods and are commonly used for dimensional stone quarrying, small tunneling projects, and secondary rock breaking, where their ease of use and cost-effectiveness are a major advantage.
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) Rods
HDD rods are a specialized type of drill rod used in trenchless technology to install pipes, conduits, and cables underground without digging a trench. These rods must possess a unique combination of strength and flexibility, as they are required to navigate complex curves and bore beneath obstacles like rivers and roads. The rods transmit both rotational torque and a high-pressure drilling fluid.
HDD rods are engineered to withstand significant bending stress and torsional forces. They are connected via robust, threaded joints that are designed for quick and secure assembly. Their primary function is to steer the pilot bore and then pull the reamer and product line back through the created borehole, making them crucial for this modern method of infrastructure installation.
Based on Material and Manufacturing
Water-Hardened Drill Rods
Water-hardened drill rods, often made from low-alloy steel like W1, are a cost-effective option. The “water-hardened” classification refers to a heat treatment process where the heated steel is quenched in water. This process results in a very hard surface but can also create a brittle core. These rods are ideal for applications where low cost and good machinability are priorities.
However, due to their lower alloy content, water-hardened rods are not as tough as other types and may not be suitable for demanding, high-stress drilling in hard, abrasive rock formations. Their use is typically limited to lighter-duty applications, smaller holes, and situations where the risk of distortion is managed through controlled use.
Oil-Hardened and Air-Hardened Drill Rods
Oil-hardened and air-hardened drill rods represent a step up in both performance and cost. These rods, made from richer alloy steels, are treated using oil or air quenching processes, respectively. This slower cooling process reduces the risk of distortion and internal stresses, resulting in a more uniform hardness and greater toughness throughout the rod.
These higher-grade rods are built for durability and are well-suited for heavy-duty drilling in challenging conditions. The superior material properties and manufacturing processes of these rods provide better wear resistance and a longer service life, making them the preferred choice for professional-grade mining, tunneling, and construction projects.
Based on Drilling Rig Type
Rotary Drill Rods
Rotary drill rods are specifically designed for rotary drilling rigs, which primarily use rotational force and downforce to grind away rock. These rods do not transmit percussive energy. Instead, their main function is to deliver rotational torque and weight to the cutting bit. They often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle the high torsional stress and bending forces encountered in this drilling method.
Rotary rods are crucial for drilling large-diameter holes in softer rock formations, soil, and for oil and gas exploration. The connections are typically threaded and sealed to handle high-pressure drilling fluids, which are used to cool the bit and flush cuttings out of the borehole, making them an essential part of the drilling fluid circulation system.
Core Drill Rods
Core drill rods are a specialized type of rotary rod used for diamond core drilling. This method is used to retrieve a cylindrical sample of rock, known as a core, for geological analysis. These rods are designed to be lightweight yet strong, and they have a hollow center to accommodate the core barrel and the rock core as it is being drilled.
The connections on core drill rods are precision-engineered to be smooth and free from any imperfections that could snag or damage the core as it moves up the drill string. The rods are designed to maintain a consistent hole size and ensure the integrity of the rock sample, which is paramount for accurate geological surveys and mineral exploration.
How to Choose Suitable Drill Rods?
Choosing the right drill rod is a critical decision that directly impacts drilling efficiency, safety, and project costs. The correct rod must be perfectly suited to the specific demands of your operation.
Drilling Method and Rig Compatibility
The rod must match your drilling method, whether it’s top-hammer, DTH, or rotary. Ensure the rod’s thread type and size are compatible with your specific drill rig and other components, such as the shank adapter and drill bit. A proper fit is essential.
Geological Conditions
The type of rock you’re drilling into is a major factor. Hard, abrasive rock requires rods made from high-strength, wear-resistant steel with specialized heat treatments. Softer formations may allow for a different, more cost-effective rod.
Hole Depth and Diameter
Consider the required depth and diameter of your holes. Deeper drilling often necessitates longer rods with higher rigidity to prevent deviation. A larger hole diameter may require a larger diameter rod to ensure efficient flushing and stable drilling.
Connection and Body Type
Decide between extension rods with couplings or MF rods. MF rods offer a more rigid connection, while extension rods provide more flexibility in a modular drill string. The body type, either round or hexagonal, should be chosen based on the need for rigidity and flushing efficiency.
Material and Manufacturing Quality
The quality of the steel and the manufacturing process are paramount. Look for rods made from premium alloy steel with advanced heat treatments like carburizing. This ensures the rod has the necessary hardness, toughness, and longevity to withstand demanding conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of various drill rod types is essential for successful drilling operations. Each rod—whether for water wells, mining, exploration, or directional drilling—is specialized to meet unique geological and operational demands.
Choosing the correct drill rod not only optimizes performance and efficiency but also significantly enhances safety and extends the lifespan of your equipment. Matching the rod to the specific task ensures precision and cost-effectiveness in any drilling project.
For a reliable supply of high-quality drilling tools, consider Sinodrills. We offer a comprehensive selection of wholesale drill rods designed to meet diverse industry needs, ensuring you have the right tool for every job.