Drag bits are essential tools in various drilling operations, from water well drilling to mining and construction. Selecting the appropriate drag bit is crucial for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This blog explores the different types of drag bits available.
Understanding the unique characteristics and applications of each drag bit type is key to optimizing your drilling performance. We’ll delve into their designs, materials, and how to choose the right bit for specific geological conditions and project requirements.
What are Drag Bits
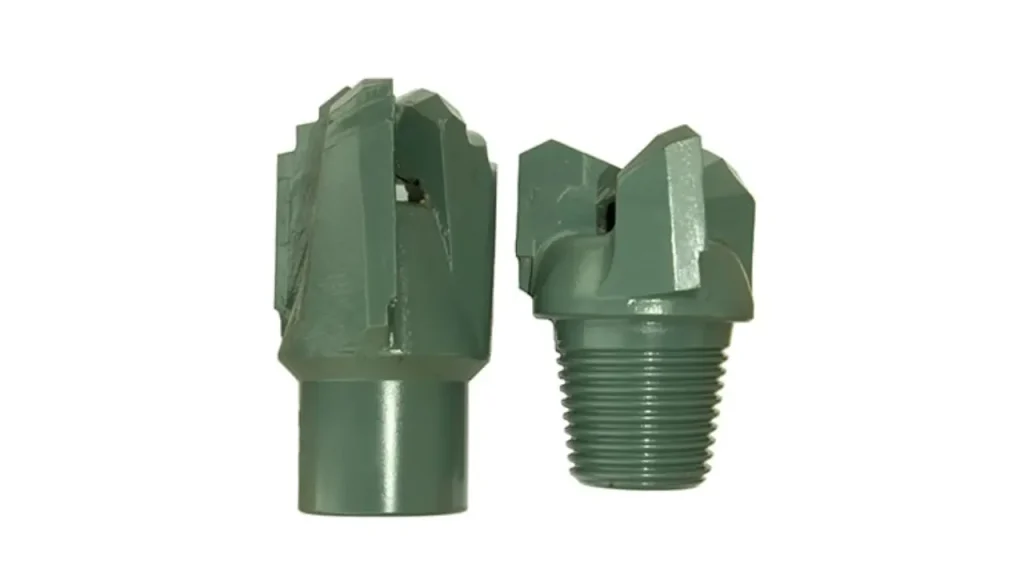

A drag bit is a type of drill bit specifically designed for drilling in soft, unconsolidated formations such as sand, clay, shale, and some soft rock.
Unlike rotary bits with moving parts, drag bits utilize fixed blades, often tipped with tungsten carbide, to shear and scrape away the formation material.
These drag bits are commonly employed in applications like water well drilling, mining, geothermal exploration, and environmental drilling, particularly for creating pilot holes where the generated cuttings are easier to log and manage. While effective in soft ground, they are not suitable for drilling through coarse gravel or hard rock formations.
Types of Drag Bits
Drag bits come in various designs, each tailored for specific drilling conditions and ground types. Understanding the distinctions between them is key to optimizing drilling performance and ensuring project success.
Here are some widely used types of drag bits that we can make in the following:
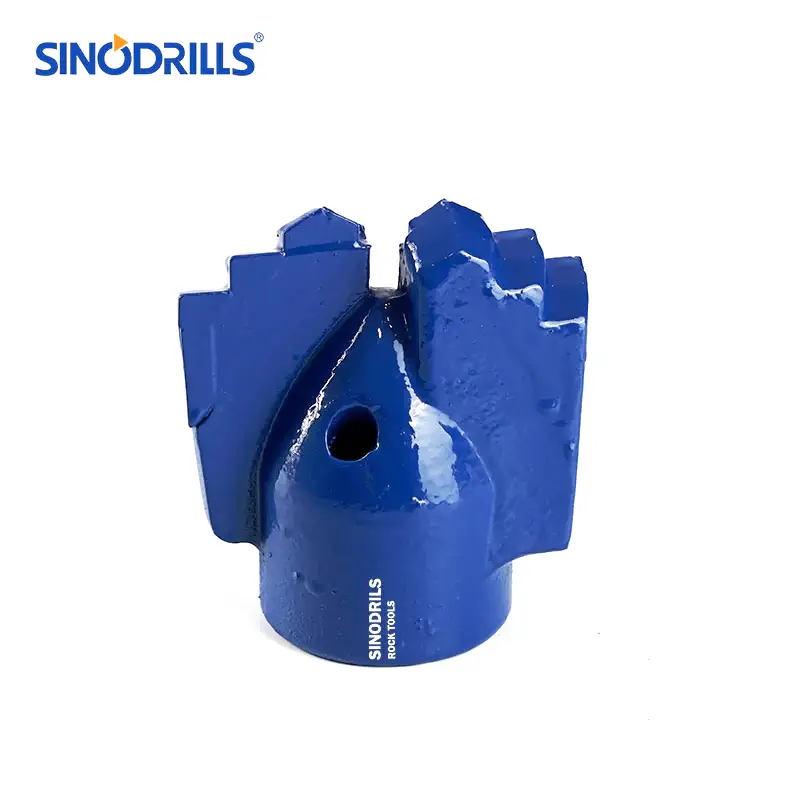
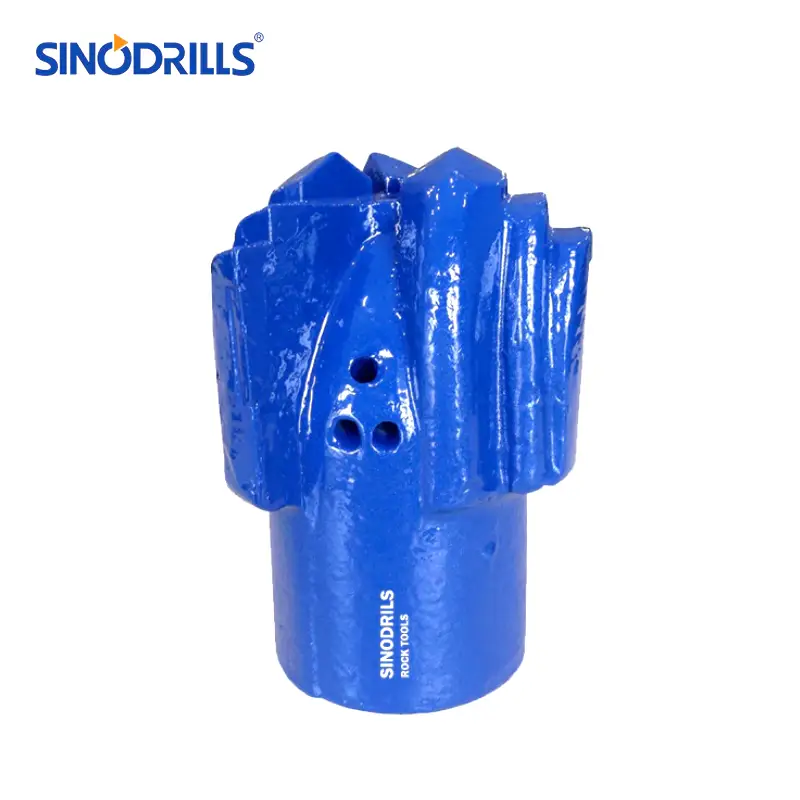
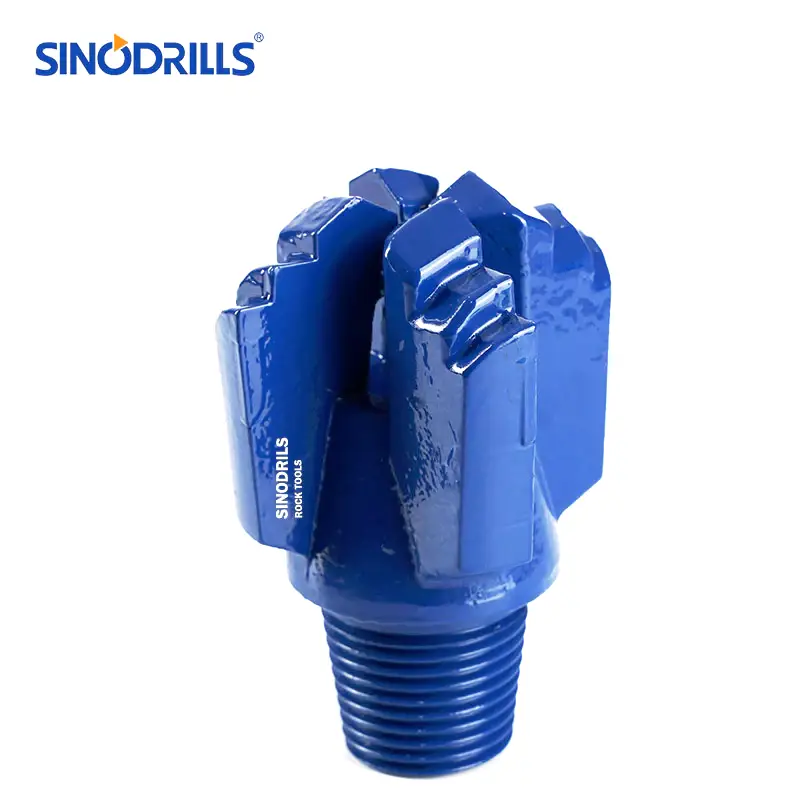
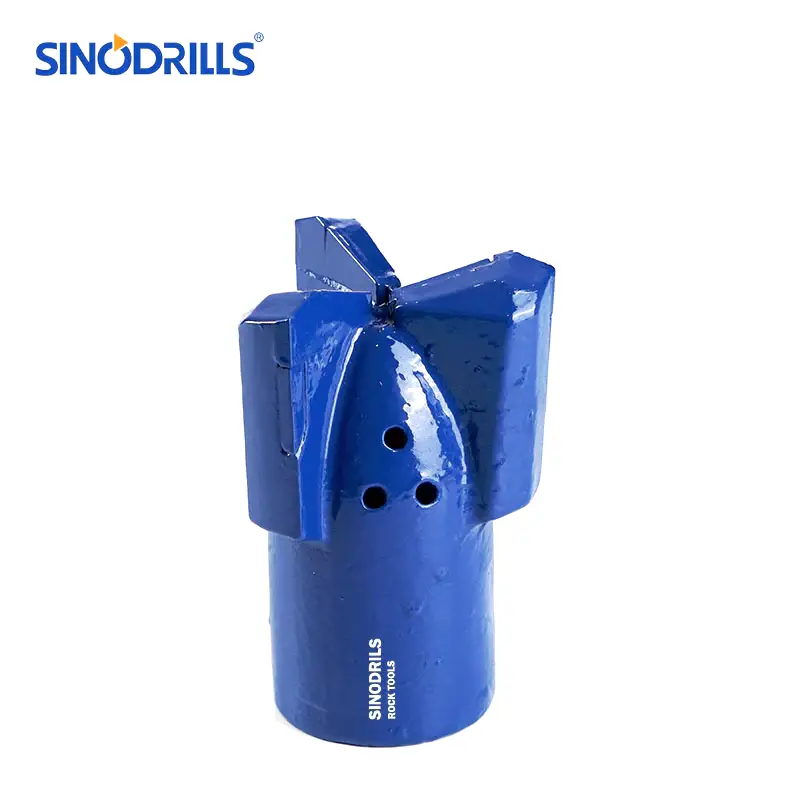
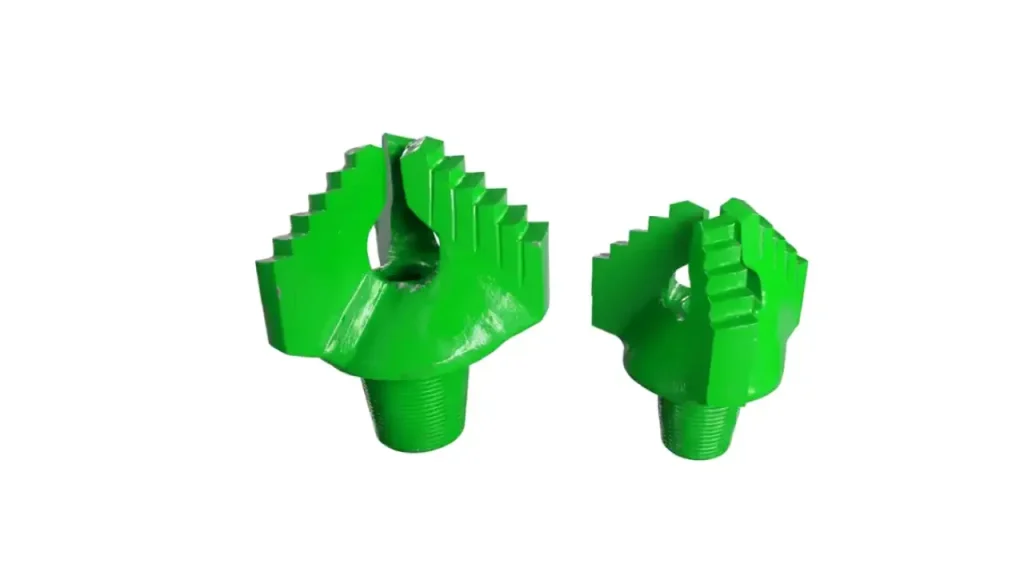
Step Drag Bits
Recommended Step Drag Bits
Step drag bits are characterized by their stepped profile, where each cutting blade is set at a different depth, creating a series of cutting edges. This design allows for a more aggressive cutting action and efficient material removal.
Features: They typically have multiple blades, often three or four, arranged in a spiral or radial pattern. The steps on the blades are designed to break up and remove cuttings effectively, preventing bit balling in sticky formations. The tungsten carbide inserts are strategically placed on the leading edges of these steps.
Benefits: The stepped design provides excellent penetration rates in soft to medium formations and is highly effective at clearing cuttings. They are less prone to “balling up” in sticky clays and shales, which can be a common issue with other bit types. Their robust construction also contributes to a longer bit life in appropriate conditions.
Uses: Stepped drag bits are widely used for drilling water wells, shallow oil and gas wells, and geotechnical investigations in formations like clay, soft shale, and unconsolidated sands. They are also suitable for various mining applications where soft overburden needs to be drilled.
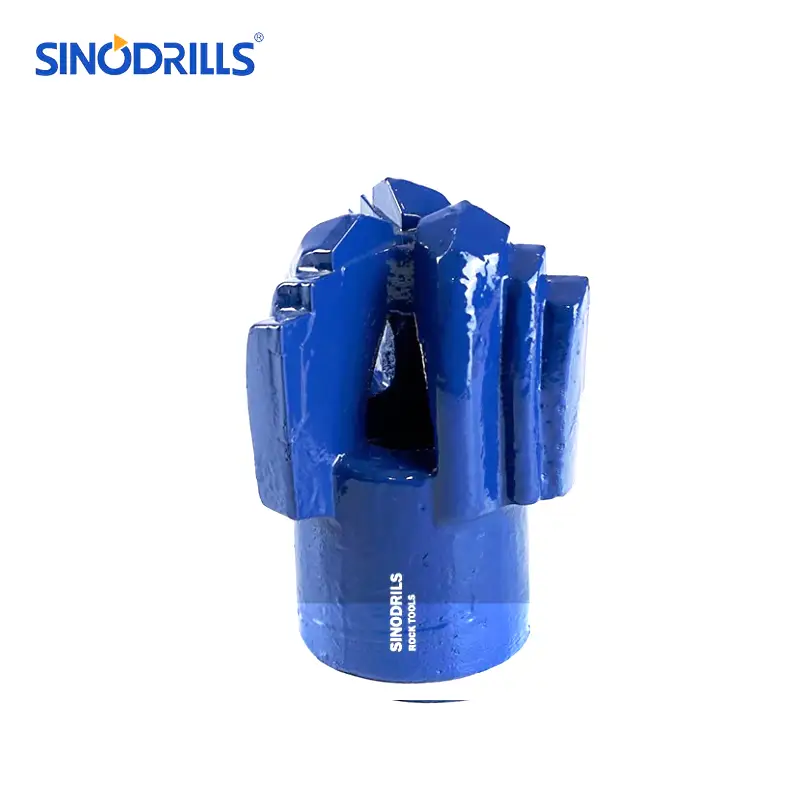
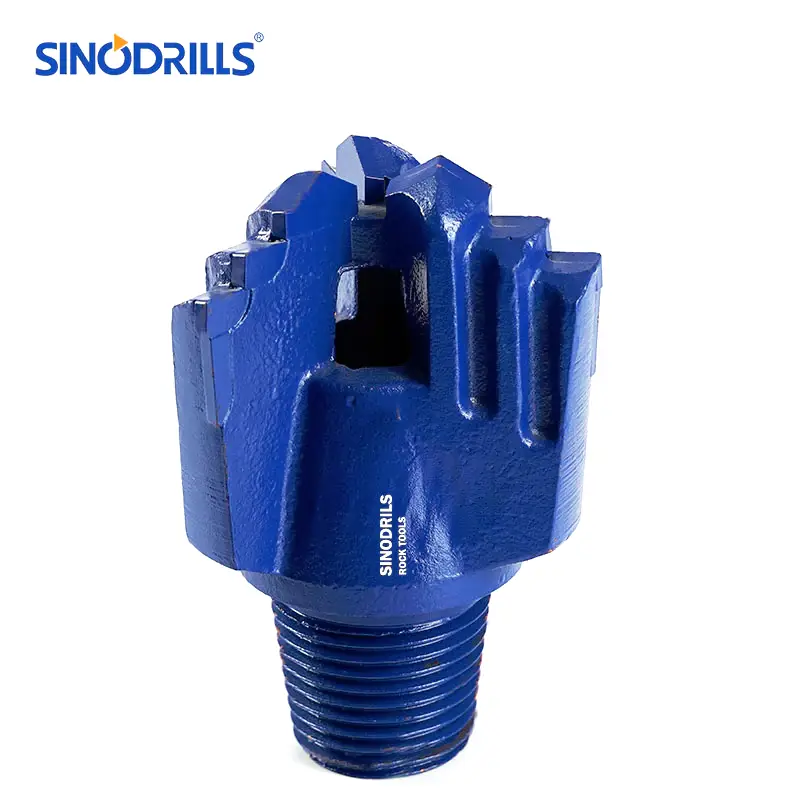
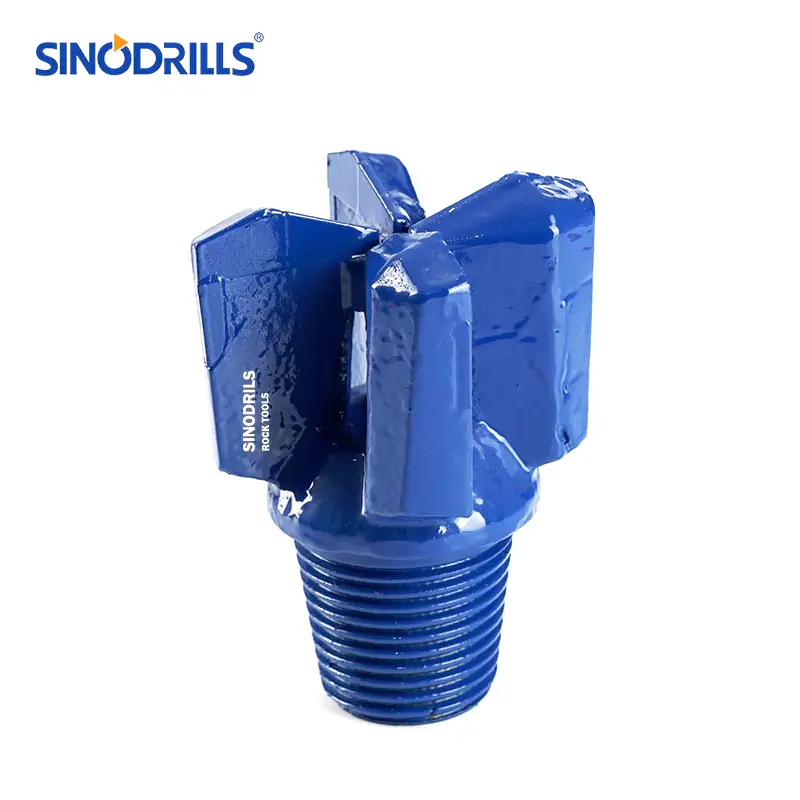
Chevron Drag Bits
Recommended Chevron Drag Bits
Chevron drag bits derive their name from the V-shaped or chevron pattern of their cutting blades. This unique geometry is designed for optimal fluid flow and efficient cutting in specific formation types.
Features: Chevron bits typically feature two or three wings or blades arranged in a chevron pattern. The angle of the “V” can vary, influencing the aggressiveness of the cut. They often have large junk slots between the blades to facilitate the easy evacuation of cuttings and prevent clogging, especially when drilling with air.
Benefits: The chevron design excels at providing stability and maintaining a straight hole, particularly in formations that might cause other bits to wander. Their large waterways and junk slots contribute to efficient flushing of cuttings, reducing the risk of regrinding and increasing penetration rates. They are also known for their durability.
Uses: Chevron drag bits are highly effective in unconsolidated to semi-consolidated formations, including soft to medium shales, limestones, and sandstones. They are frequently employed in shallow oil and gas drilling, mineral exploration, and environmental drilling where maintaining hole integrity is paramount.
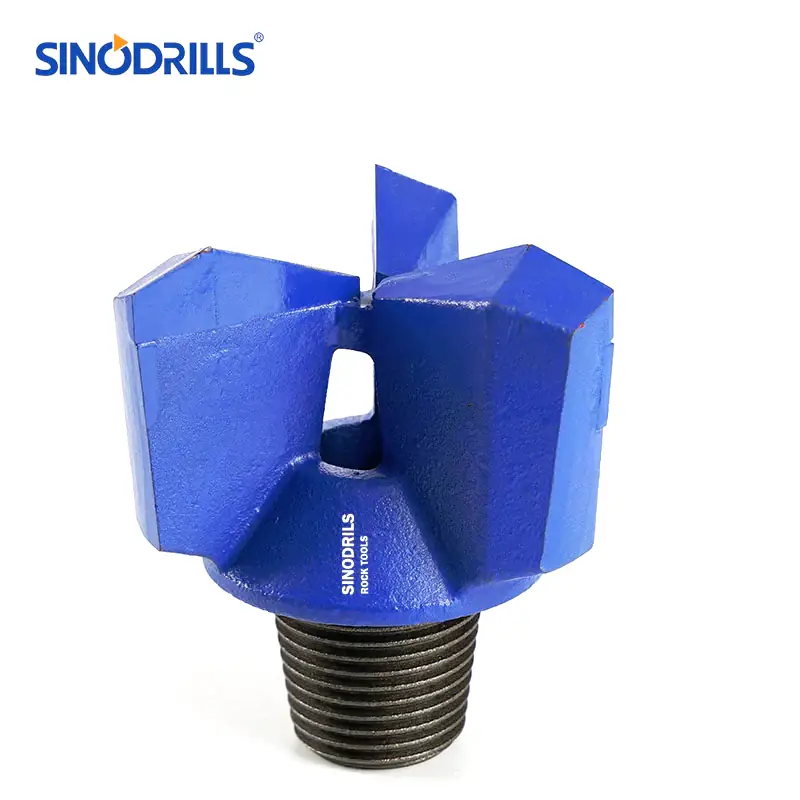
Blade Drag Bits

Blade drag bits, sometimes referred to as fishtail bits, are characterized by their simpler, flatter blade design. They are among the most basic and economical types of drag bits.
Features: These bits typically have two or more flat, fixed blades extending from the bit body. The cutting edges are usually faced with tungsten carbide inserts or hardfacing for improved wear resistance. The blades can be straight or slightly angled, and the junk slots are generally large to allow for good fluid circulation.
Benefits: Blade drag bits are cost-effective and relatively simple to manufacture. They offer good penetration rates in very soft formations and are particularly useful in situations where a large diameter hole is needed quickly. Their straightforward design makes them easy to maintain and repair in the field.
Uses: Blade drag bits are primarily used in very soft, unconsolidated materials such as loose sand, soft clay, and mud. They are common in water well drilling in alluvial deposits, agricultural irrigation projects, and some environmental sampling applications where the ground is known to be very pliable. They are not recommended for any hard or abrasive formations.
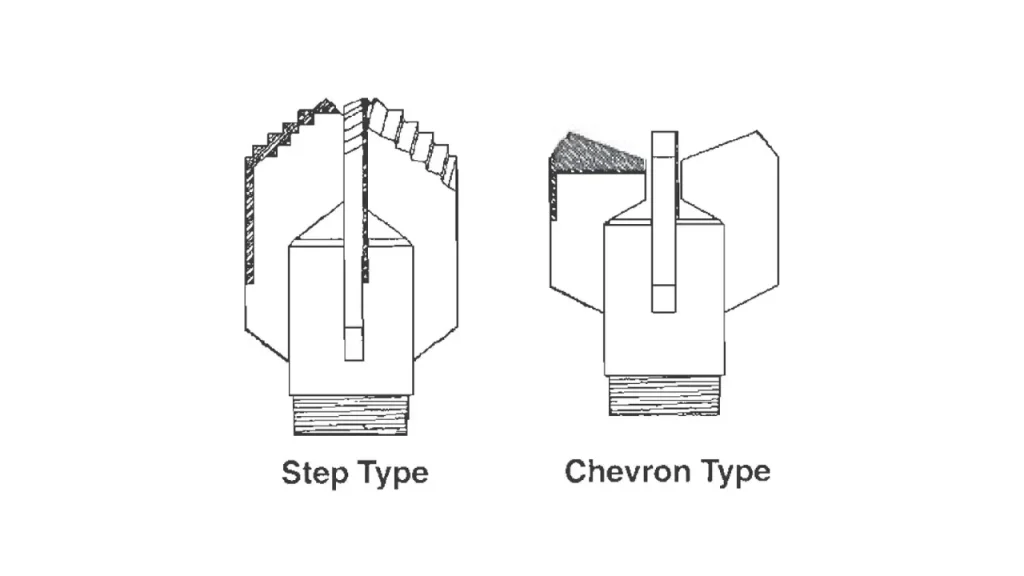
Step Drag Bit vs Chevron Drag Bit

Drag bits are a specialized type of drill bit used primarily for drilling in soft, unconsolidated formations such as sand and clay. The two most widely utilized designs are the step drag bit and the chevron drag bit, which are engineered with distinct cutting structures to optimize performance under different downhole conditions. Choosing the right one is essential for maximizing drilling efficiency and bit life, directly impacting project cost and timeline.
Step Drag Bit
The step drag bit is characterized by its tiered, stair-stepped cutting edges. This design features multiple blades with staggered cutting surfaces. This aggressive profile is specifically tailored for maximizing penetration rate in the softest, most non-abrasive geological materials.
- Design and Aggressiveness The stepped profile allows the bit to be highly aggressive, effectively shearing and tearing away soft material with each revolution. This action facilitates rapid hole making, making it the preferred choice for applications where speed in very soft ground is the main objective.
- Rate of Penetration (ROP) Step bits are renowned for delivering a higher ROP compared to other drag bit types. Their sharp, staggered cutters are optimized to quickly process large volumes of loose soil and clay, leading to significantly reduced drilling time in favorable conditions.
- Cuttings Management The open design and deep junk slots between the steps are excellent for cuttings removal. This structure prevents sticky materials, particularly soft clay, from accumulating on the bit face, a problem known as “bit balling.”
- Formation Suitability They are best suited for drilling in very loose, non-cohesive materials like sand, soft clay, and mud. Using a step bit in formations that are too hard or abrasive will lead to rapid damage and premature wear of the tungsten carbide cutters.
- Durability While fast, the step bit is less robust than the chevron design. Its cutting edges are more exposed and the structure is less reinforced, meaning it has lower durability and a shorter lifespan when encountering unexpectedly hard layers or gravel.
Chevron Drag Bit
The chevron drag bit features V-shaped cutting wings, giving it a more solid and reinforced cutting structure. This design emphasizes stability and durability over sheer speed, making it suitable for slightly more challenging, yet still soft, drilling environments.
- Design and Aggressiveness: The V-shaped pattern results in a more stable and scraping cutting action. The angle of the blades allows for a smoother cut and better directional control, reducing the chance of the bit wobbling or “walking” during drilling.
- Rate of Penetration (ROP): Chevron bits typically operate at a slower ROP than step bits. This reduced speed is a trade-off for their enhanced durability and stability, which allows them to penetrate consolidated or abrasive formations more effectively without sustaining major damage.
- Cuttings Management: This design is effective for handling cuttings in slightly consolidated or abrasive materials. The robust, wide junk slots efficiently evacuate ground-up rock and clay, minimizing the potential for regrinding and maintaining a cleaner cutting face.
- Formation Suitability: They are recommended for drilling in moderately soft to slightly consolidated formations such as soft shale, firm clay, and soft sandstones. Their sturdier construction can better withstand the mild abrasion of these harder materials.
- Durability: The chevron design is inherently more durable due to the better structural support for the cutters. This makes them a more dependable choice for formations with varying hardness or for prolonged use in semi-consolidated ground conditions.
How to Choose the Right Drag Bits
Choosing the right drag bit is paramount for drilling efficiency and project success, directly impacting penetration rates, bit life, and overall cost. A careful assessment of several key factors will guide you to the optimal selection. Understanding your drilling environment and operational goals is the first step toward making an informed decision.
Consider the following critical aspects when selecting your drag bit:
- Formation Hardness and Abrasiveness: Different formations require different bit types. For very soft and unconsolidated ground like sand or soft clay, a blade bit might suffice. As formations become progressively harder or more abrasive, such as soft shale or limestone, stepped or chevron bits with more robust carbide inserts and aggressive cutting structures are necessary to ensure effective drilling and prolong bit life.
- Desired Hole Diameter: The size of the hole you need to drill influences the available drag bit designs and their cutting structures. Larger hole diameters may require bits with more blades or specific geometries to ensure efficient cutting and cuttings removal. Ensure the bit size matches your drilling rig’s capabilities and casing requirements for a smooth operation.
- Drilling Fluid/Air Type: The medium used for flushing cuttings—whether water, mud, or air—significantly impacts bit selection. Bits with larger junk slots and optimized waterway designs are better suited for air drilling to prevent regrinding and ensure efficient chip removal. Conversely, specific mud types might necessitate different bit face designs to prevent bit balling and maintain penetration.
- Rig Capabilities and Torque/Weight-on-Bit (WOB): Your drilling rig’s available torque and ability to apply sufficient weight-on-bit are crucial. Some drag bits perform best with higher WOB, while others are more forgiving. Mismatching the bit’s requirements with your rig’s capabilities can lead to poor performance, excessive wear, or even damage to the bit or drilling equipment, hindering progress.
Why Choose Our Drag Drill Bits?
Our drag drill bits are engineered for superior performance, durability, and efficiency. Designed to meet demanding drilling conditions, they provide consistent penetration rates and long service life. We focus on quality, precision, and reliability, making our drag drill bits the ideal choice for your drilling operations.
- High Durability: Our drag drill bits are made with premium materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, ensuring they withstand harsh drilling environments and resist wear, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Efficient Drilling: Engineered for optimal cutting geometry, our bits minimize vibration and improve penetration rates, reducing drilling time, energy consumption, and operational costs while maintaining accuracy and stability.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide range of formations, our drag drill bits excel in soft to medium-hard rocks, ideal for oil, gas, geothermal, and water well drilling projects.
- Precision Design: Each bit is carefully designed for balanced weight distribution and cutting action, enhancing performance, reducing wear on the drill string, and ensuring smoother operation in uneven rock formations.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Our drag drill bits offer long-term value through durability and efficiency, reducing wear, maintenance needs, and drilling time for a cost-effective high-quality solution.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal drag bit is crucial for efficient and effective drilling. Understanding the different types—stepped, chevron, and blade—and their ideal applications ensures you achieve the best results for your specific geological conditions.
By carefully considering factors like formation hardness, desired hole size, and drilling fluid, you can significantly enhance penetration rates and bit life. This informed decision-making minimizes downtime and optimizes your overall drilling operation.
For a comprehensive selection of high-quality wholesale drag bits to meet diverse drilling demands, consider Sinodrills as your reliable supplier.